In the heart of Mexico, the nation’s last remaining glaciers are vanishing at an alarming pace. New satellite imagery reveals the stark retreat of glacial ice on the Iztaccíhuatl volcano, a towering peak just southeast of Mexico City. The glaciers that crown this iconic stratovolcano have long been a vital source of freshwater and a symbol of Mexico’s high-altitude ecosystems — but they are now on the brink of extinction.
According to scientists from the National Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM), the country’s few remaining glaciers are expected to disappear within five years. The combined forces of rising temperatures, persistent drought, and volcanic activity are accelerating ice loss, with profound implications for biodiversity, local communities, and water availability across central Mexico.
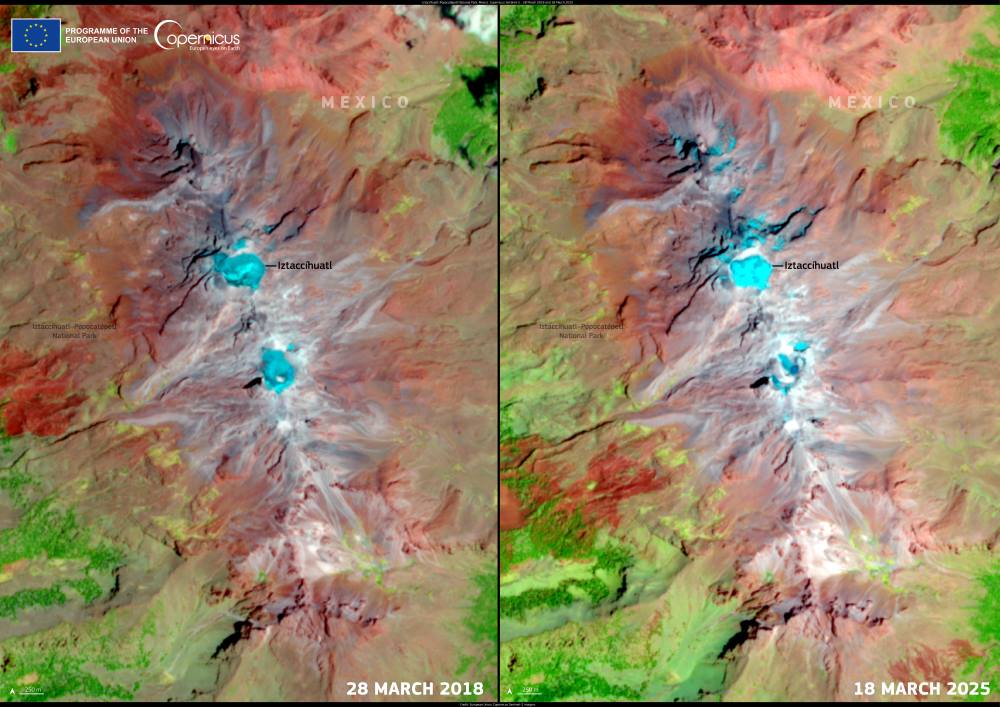
In these two Copernicus Sentinel-2 satellite images — taken on 28 March 2018 and 18 March 2025 — the dramatic retreat of glacial cover in the Iztaccíhuatl–Popocatépetl National Park is clearly visible. The shrinking white patches on the volcano’s slopes illustrate just how quickly Mexico’s ice reserves are melting away.
The Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission, operated by the European Space Agency, provides high-resolution optical imagery that is freely accessible for environmental monitoring. Its consistent and detailed views of Earth’s surface make it an indispensable tool for tracking changes in glaciers, forests, coastlines, and agricultural regions.
For researchers, the satellite data not only document the speed of glacial retreat but also inform conservation and climate resilience strategies. “Adiós a los glaciares mexicanos” may be more than a headline — it’s a warning signal that the loss of high-mountain ice in Mexico is no longer a distant threat but an imminent reality. As these glaciers vanish, so too does a crucial water source and a key part of Mexico’s natural heritage.
Featured image credit: European Union, Copernicus Sentinel-2 imagery



