In autumn 2024, Australia witnessed a concerning rise in bushfire activity, leading to a significant increase in carbon emissions. The fires, which have been ravaging large parts of the country, have contributed to above-average carbon emissions, disrupting the natural balance and intensifying the ongoing climate crisis.
The region of Queensland has been particularly impacted, recording its highest carbon emissions since 2011.
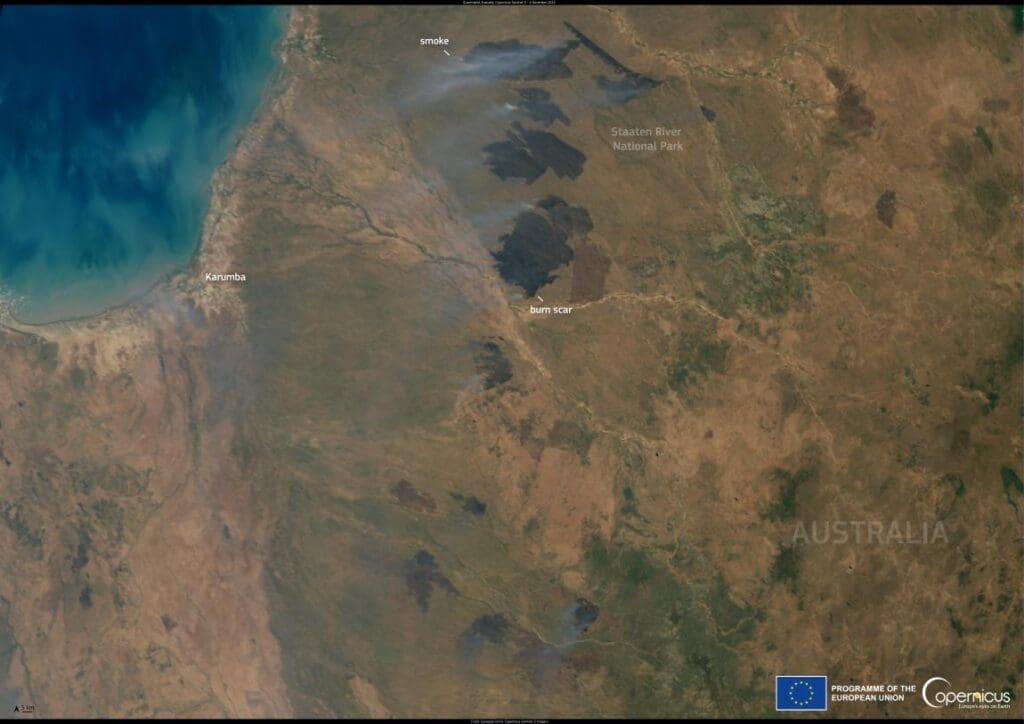
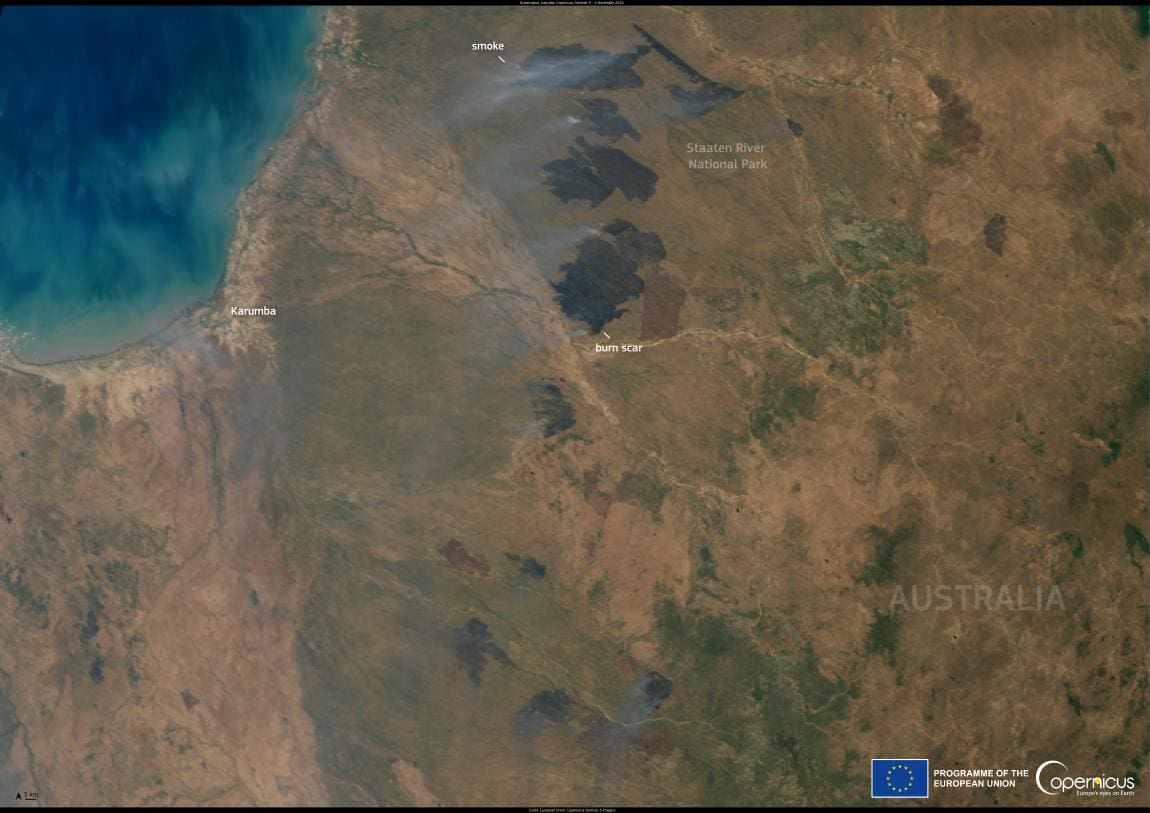
This image, acquired by one of the Copernicus Sentinel-3 satellites on 4 November 2024, shows multiple active wildfires in the Staaten River National Park in Queensland.
As fire-prone regions of Australia face worsening conditions, intensified by rising temperatures and prolonged droughts, the bushfires have reached alarming levels. Satellite imagery and ground reports reveal vast swathes of land scorched by flames, with plumes of smoke spiraling into the atmosphere. These fires not only devastate ecosystems and displace communities but also release massive amounts of carbon dioxide, further exacerbating the planet’s climate emergency.
Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service (CAMS) provides accurate and timely information on the location, intensity, and estimated emissions of wildfires on a global scale. These insights support essential decision-making on environmental and health challenges.
Featured image credit: European Union, Copernicus Sentinel-3 imagery