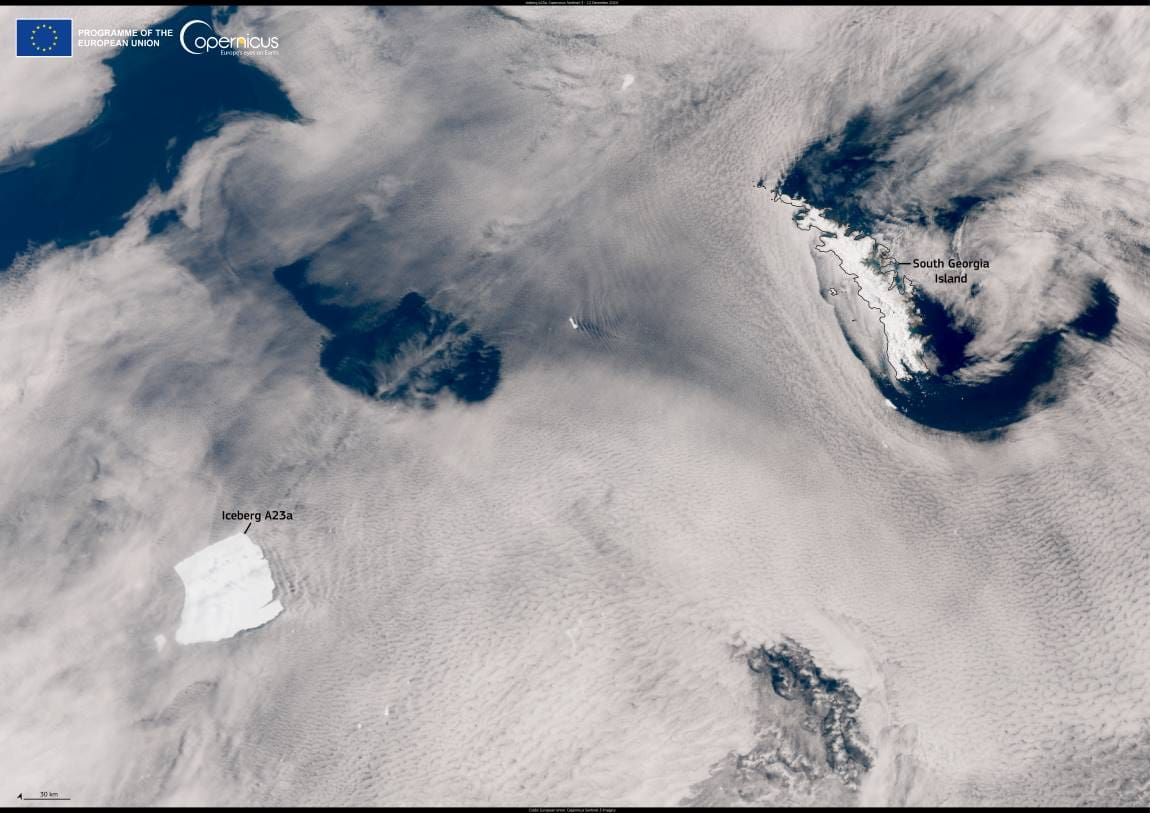
A23a, the world’s largest iceberg, has begun a significant journey after decades of remaining stationary. Measuring nearly 3,500 square kilometers in surface area and 400 meters thick, this massive ice block originally calved from the Filchner-Ronne ice shelf in West Antarctica in 1986.
For over 30 years, it was grounded on the seafloor of the Antarctic Ocean, effectively frozen in place.
Recent shifts in ocean dynamics have set A23a adrift, moving northward toward the southern Atlantic Ocean. Oceanographers predict that as it encounters warmer waters, the iceberg will gradually fragment into smaller pieces and eventually melt. This process highlights the natural lifecycle of Antarctic icebergs and the influence of ocean currents on their trajectories.
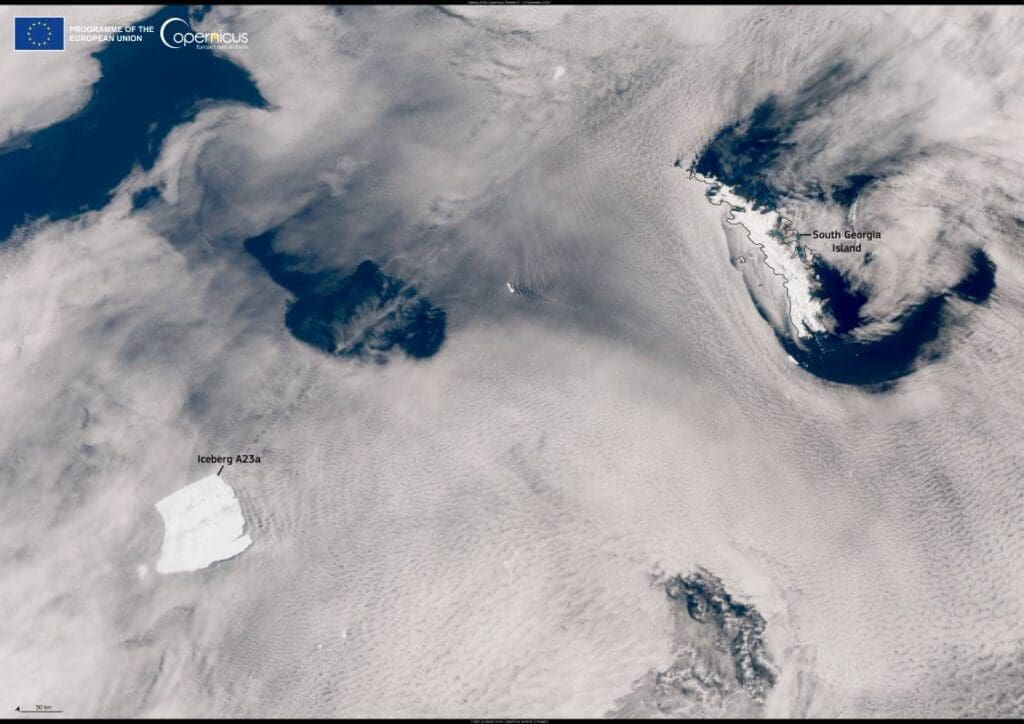
The image capturing this dramatic movement was taken on December 12, 2024, by a Copernicus Sentinel-3 satellite. At the time, the iceberg was located approximately 400 kilometers southwest of South Georgia, a region known for its significant marine biodiversity.
Satellite data from the Copernicus program plays a critical role in monitoring such remote environments. These observations are vital for understanding iceberg dynamics and their potential impact on ecosystems and sea level rise. The open availability of Copernicus data ensures scientists worldwide can track icebergs like A23a and study their broader implications on climate systems.
Featured image credit: European Union, Copernicus Sentinel-3 imagery