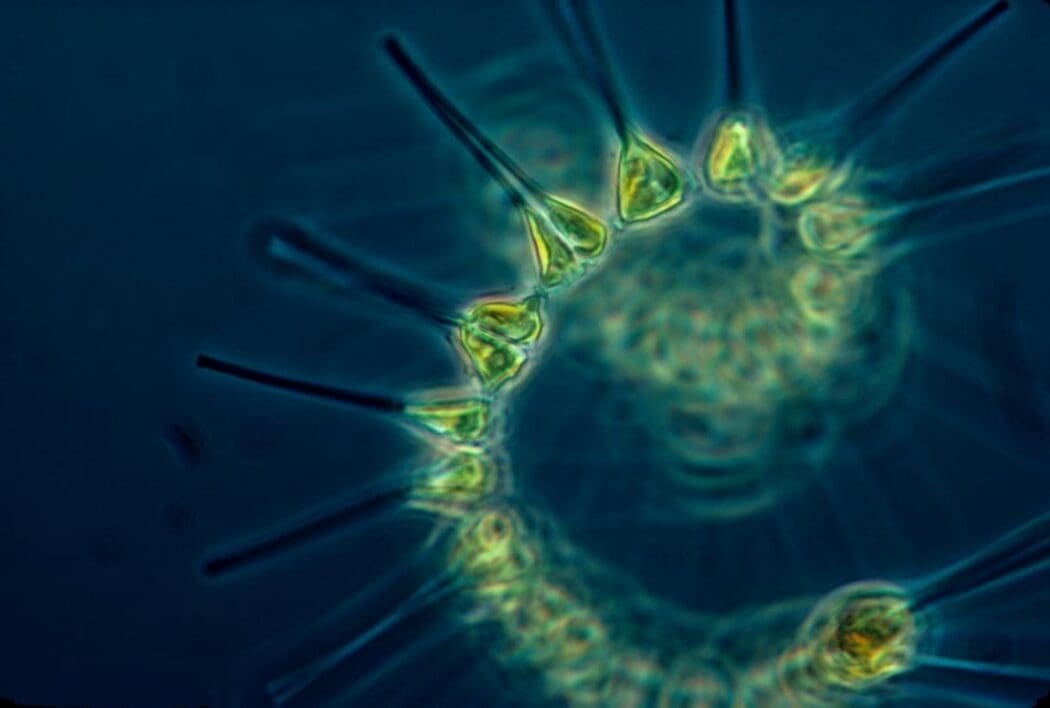
The tiny phytoplankton that drive oxygen production and carbon storage in Earth’s oceans are revealing how they navigate their ever-changing underwater world.
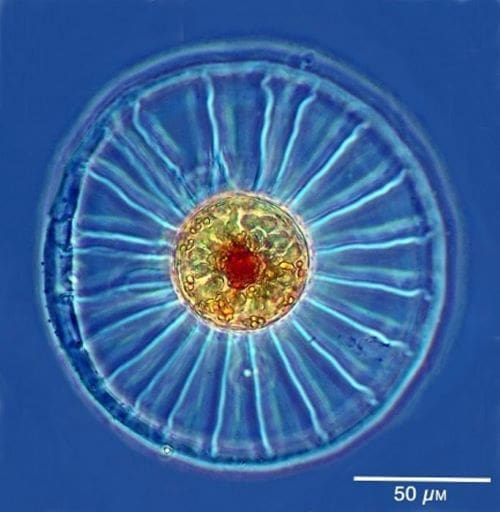
Researchers from the CNRS and Sorbonne University have identified a critical mechanism: light-sensing molecules called phytochromes, embedded in the genomes of diatoms, a prominent group of phytoplankton. This discovery sheds light on the strategies microalgae use to adapt to turbulent aquatic environments and shifting light conditions.
Diatoms, like terrestrial plants, perform photosynthesis, contributing significantly to the planet’s oxygen production and carbon capture. However, maintaining this balance in the mixed layers of the ocean requires sophisticated adaptations.
Phytochromes act as “eyes” for these microalgae, detecting subtle changes in the light spectrum as it filters through the water column. By interpreting these variations, diatoms determine their vertical position and adjust their biological activities, particularly photosynthesis.
The study, published in Nature, shows the role of phytochromes in high-latitude, temperate, and polar regions – areas prone to strong water mixing and marked by dramatic seasonal light variations. Through environmental genomic data from the Tara Oceans marine sampling campaigns, researchers discovered that phytochromes are exclusively present in diatoms inhabiting zones beyond the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn. These regions’ pronounced seasonality appears to demand a mechanism for tracking seasonal changes, with phytochromes enabling diatoms to measure shifts in day length.
This revelation not only illuminates the ways phytoplankton perceive and respond to their environment but also highlights their adaptability in the face of environmental changes. By integrating data from both laboratory experiments and natural marine settings, the research paves the way for a deeper understanding of marine ecosystems and their resilience in a rapidly changing world.
Journal Reference:
Duchêne, C., Bouly, JP., Pierella Karlusich, J.J. et al. ‘Diatom phytochromes integrate the underwater light spectrum to sense depth’, Nature (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-08301-3
Article Source:
Press Release/Material by CNRS
Featured image credit: NOAA | Unsplash