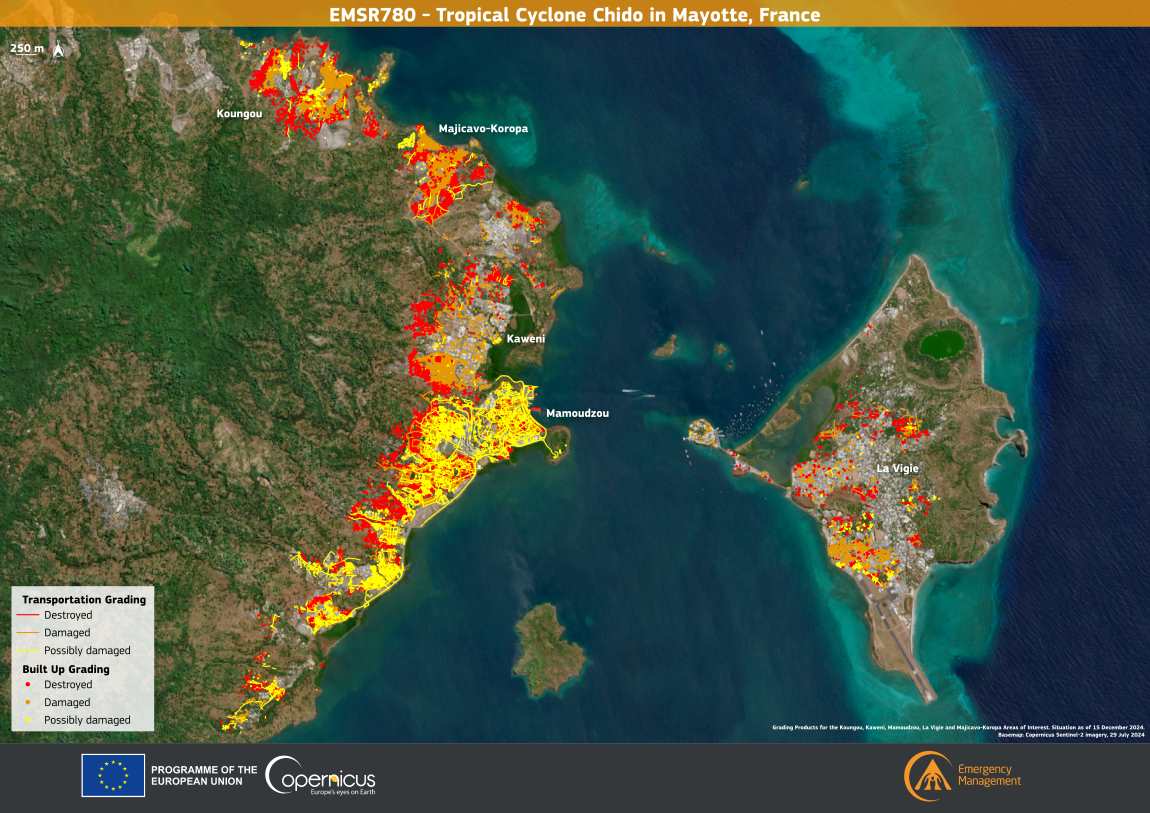
Cyclone Chido, the most powerful storm to hit Mayotte in nearly a century, left a trail of devastation on December 14, 2024.
The French archipelago in the Indian Ocean, located near Madagascar, endured winds surpassing 220 km/h as the Category 4 storm tore through the islands. Homes and vital infrastructure were reduced to rubble, with roads and electrical grids rendered inoperable, hindering rescue and recovery efforts.
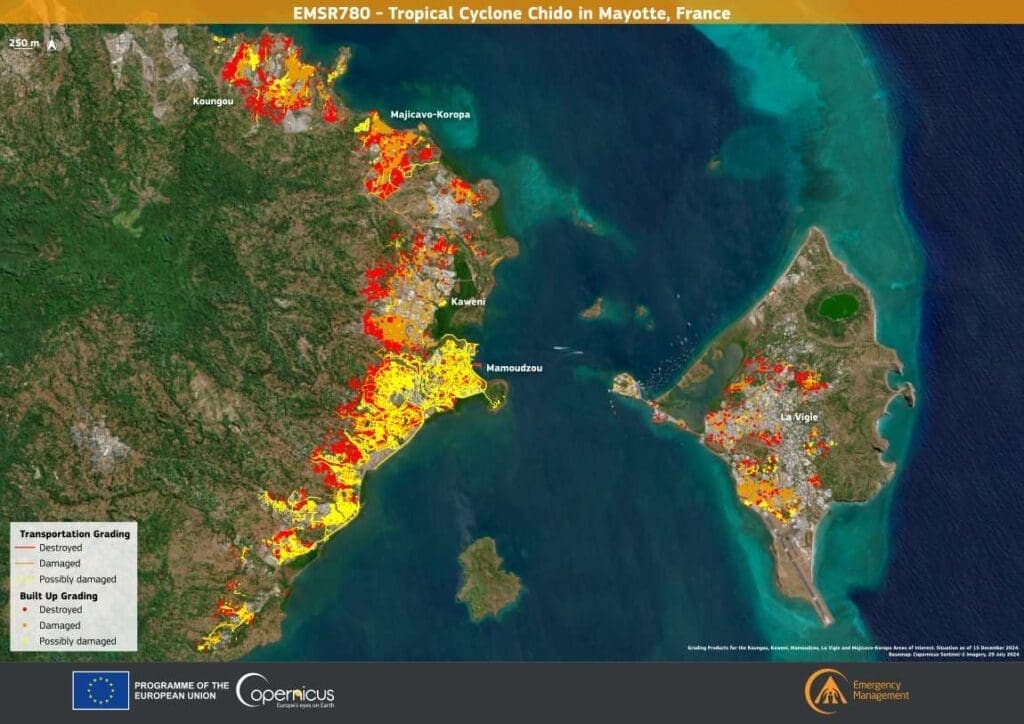
French authorities report significant loss of life, with hundreds of casualties feared, while survivors contend with severe shortages of essential resources such as electricity, clean water, and humanitarian aid. Assistance teams have been mobilized from mainland France and the neighboring French territory of Reunion, bringing much-needed support to the recovery efforts.
The Copernicus Emergency Management Service (CEMS) has activated EMSR780 to map the damage and guide aid delivery. The visualization accompanying the activation highlights the extent of destruction, with detailed assessments of buildings and transportation networks in the affected regions. These resources are instrumental in coordinating a response to one of Mayotte’s most catastrophic events in recent history.
More information on the CEMS response can be found on their official website.
Featured image credit: European Union, Copernicus Emergency Management Service Data