By National Agriculture and Food Research Organization (NARO), Japan
Concern about the effects of PFAS are of increasing globally. Also there is no accurate method for analyzing multiple PFAS in soil. Hence, a team of PFAS researchers led by NARO et.al sought to develop a stable and accurate method for analyzing multicomponent PFAS in the soil (Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries – MAFF project).
Unlike the PFAS analysis method for water samples, it is difficult to ensure the extraction efficiency of the target PFAS in diverse soil samples. In Japan, there are 381 soil types, with volcanic ash soils being the predominant. Since these soils possess high carbon content, efficient multicomponent PFAS extraction is challenging. The research team has developed a novel method for PFAS analysis using typical Japanese Andosols and brown lowland soils and published a manual ‘Determination of per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in the soil’ (DRAFT METHOD 202201).
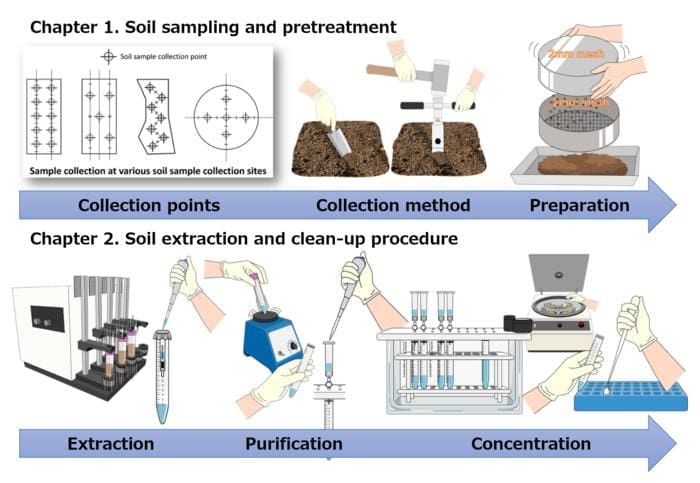
Characteristics of the analytical method
●Simultaneous analysis of 30 different PFAS, including PFOA, PFOS, and perfluorohexane sulfonate (PFHxS) is possible.
These representative PFAS which is included in overseas assessments of drinking and environmental water can be analyzed simultaneously in soil.
●Simplified process for multiple sample analysis
To reduce analysis time and cost, insoluble materials are removed via centrifugation, and the solution is transferred through decantation.
●Easy-to-understand visual explanation of the analysis procedure.
All processes from sample preparation to PFAS content measurement, including soil sampling and pretreatment, are clearly explained via illustrations.
●Immediate analysis possible by specifying condition settings .
The analytical parameters that are compatible with the models used are included in the manual with the cooperation of Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) manufacturers.
- THEMATIC CHAPTERS
This manual consists of four chapters: (1) soil sampling and pretreatment; (2) extraction, purification, and concentration of PFAS from soil samples; (3) PFAS content assessment using LC-MS/MS; and (4) reagents and measurement conditions for reference.
- PURPOSEFUL SELECTION
This manual allows users to implement PFAS analysis according to their objectives, by selecting targets from 30 types of PFAS, which are classified into three groups based on their measurement needs.
- USEFUL APPENDIX
This manual provides check sheets for each step of the sampling, extraction, and purification processes. This enables the user to proceed without omitting any process during the analysis. In addition, the manual provides simple illustrations explaining the selection of soil sample collection points, collection methods, and handling of testing equipment and instruments used in all processes from sample pretreatment to PFAS content measurement. Hence it will be user-friendly even for those conducting PFAS analysis for the first time.
- ANALYST-FRIENDLY
This manual assumes routine analysis that can quickly and efficiently analyze a large number of soil samples. In addition, by considering the safety of the analyst, the manual describes the use of the minimum amount of test chemicals required and procedures such as decanting to reduce time and workload.
- MANUFACTURERS’S BACKUP
Measurement method files for the main models of the LC-MS/MS instruments used in the analysis were prepared in cooperation with the manufacturers (Nihon Waters Corporation, Agilent Technologies Inc., and Shimadzu Corporation). Users can start the analysis immediately by referring the method files and the manuals of each instrument without the need to examine or adjust the measurement conditions.
- HIGH RECOVERY RATE
In this manual, recovery test results for the addition of internal standard substances in andosol and brown lowland soil, which are common agricultural soils in Japan were provided. Based on this it can be assured that PFAS can be analyzed in a highly efficient and stable manner. For example, the four main compounds of Group 1 (PFHxS, PFOS, PFOA, and perfluorononanoic acid) were extracted and listed. The average recovery rate obtained by dividing the measured value by the added concentration was in the range of 98–116% for andosol and 94–108% for brown lowland soil, with standard deviations ranging 3.09–5.65 and 4.38–5.79, respectively, indicating good results.
- FREE OF CHARGE
In order to contribute to an early solution to the global PFAS problem, the manual and measurement method files are provided for free on the NARO website. The measurement method files can be acquired from the webpages of the device manufacturers (the URLs are listed in the manual).
Currently, 23 institutes in Japan, including private and national research institutes, have started interlaboratory studies using this manual. Also procedures are underway in China, Korea, Hong Kong, the EU, and the USA.
NARO is the core institute in Japan for conducting research and development in a wide range of fields, from basic to applied, for the development of agriculture and food industries.
More information: NARO-MAFF, ‘Determination of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in soil’ (DRAFT METHOD 202201; ver. 1.1, 2024). NORA Press Release. Featured image credit: Freepik




