By Chandan KHANNA | AFP
Bridgetown, Barbados (UPDATED) – Much of the southeast Caribbean was on alert Sunday as Beryl strengthened into the first hurricane of the 2024 Atlantic season, with forecasters warning of an “extremely dangerous” Category 4 storm.
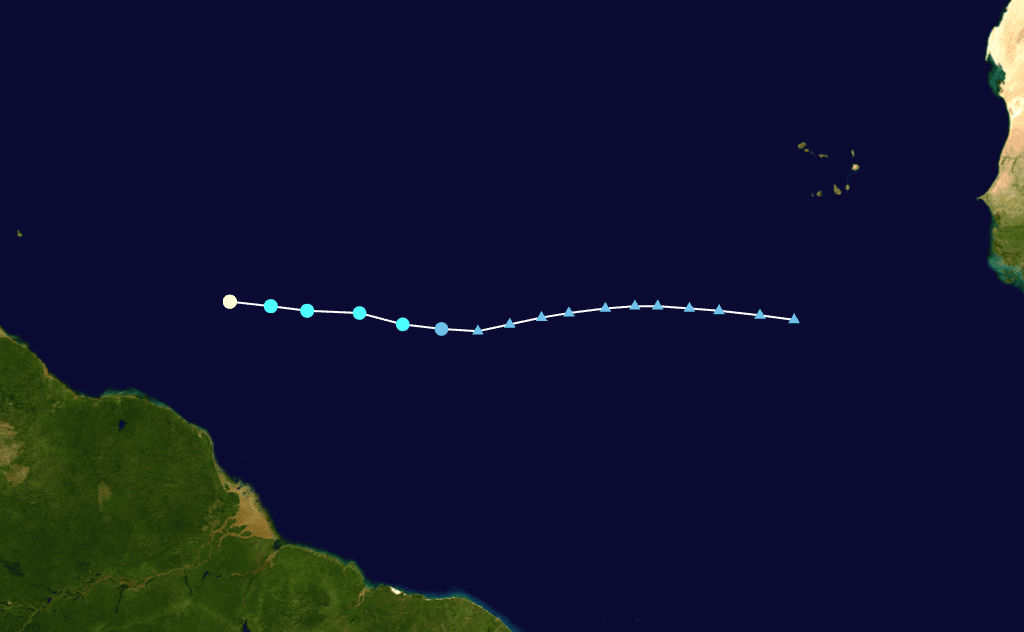
The US National Hurricane Center (NHC) said Beryl — currently churning in the Atlantic Ocean about 465 miles (750 kilometers) east of Barbados — was expected to bring “life-threatening winds and storm surge” when it reaches the Windward Islands early Monday.
Warning the storm is “continuing to rapidly intensify,” the NHC forecast it would become an “extremely dangerous Category 4 hurricane” by the time it hit Caribbean communities.
Barbados, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, and Grenada were all under hurricane warnings, while tropical storm warnings or watches were in effect for Martinique, Tobago and Dominica, the NHC said in its latest advisory.
Cars were seen lined up at gas stations Saturday in the Barbadian capital Bridgetown, while supermarkets and grocery stores were crowded with shoppers buying food, water and other supplies. Some households were already boarding up their properties.
A Category 3 or higher on the Saffir-Simpson scale is considered a major hurricane, and a Category 4 storm packs sustained winds of at least 130 miles per hour (209 kilometers per hour).
The NHC said that by around 5:00 am (0900 GMT) Sunday, Beryl’s maximum sustained winds had increased to nearly 100 mph, with higher gusts.
Such a powerful storm forming this early in the Atlantic hurricane season — which runs from early June to late November — is extremely rare, experts said.
“Only five major (Category 3+) hurricanes have been recorded in the Atlantic before the first week of July. Beryl would be the sixth and earliest this far east in the tropical Atlantic,” hurricane expert Michael Lowry posted on social media platform X.
“Hurricane conditions are expected in the hurricane warning area beginning early on Monday,” the NHC said, warning of heavy rain, flooding and storm surge that could raise water levels as much as nine feet (2.7 meters) above normal.
“Devastating wind damage is expected where the eyewall of Beryl moves through portions of the Windward Islands,” the NHC said, indicating wind speeds in some locations could be 30 percent stronger than those listed in their advisory.
The US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration said in late May that it expects this year to be an “extraordinary” hurricane season, with up to seven storms of Category 3 or higher.
The agency cited warm Atlantic ocean temperatures and conditions related to the weather phenomenon La Nina in the Pacific for the expected increase in storms.
Extreme weather events including hurricanes have become more frequent and more devastating in recent years as a result of climate change.
bur-st-mlm/rsc/smw
© Agence France-Presse
Featured image credit: OhHaiMark | Public domain