This data visualisation from the Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) presents the precipitation anomaly for Europe in March 2025. It reflects clear regional contrasts, with wetter-than-average conditions over southwestern Europe and drier-than-average conditions across much of the north and southeast.
Much of the Iberian Peninsula, as well as parts of southern France, experienced significantly above-average rainfall. This was driven by a sequence of severe weather events that swept across the region during the month, bringing heavy downpours and resulting in widespread flooding. Some areas faced repeated storms that contributed to saturated soils and river flooding, causing damage to infrastructure and disruptions to local communities.
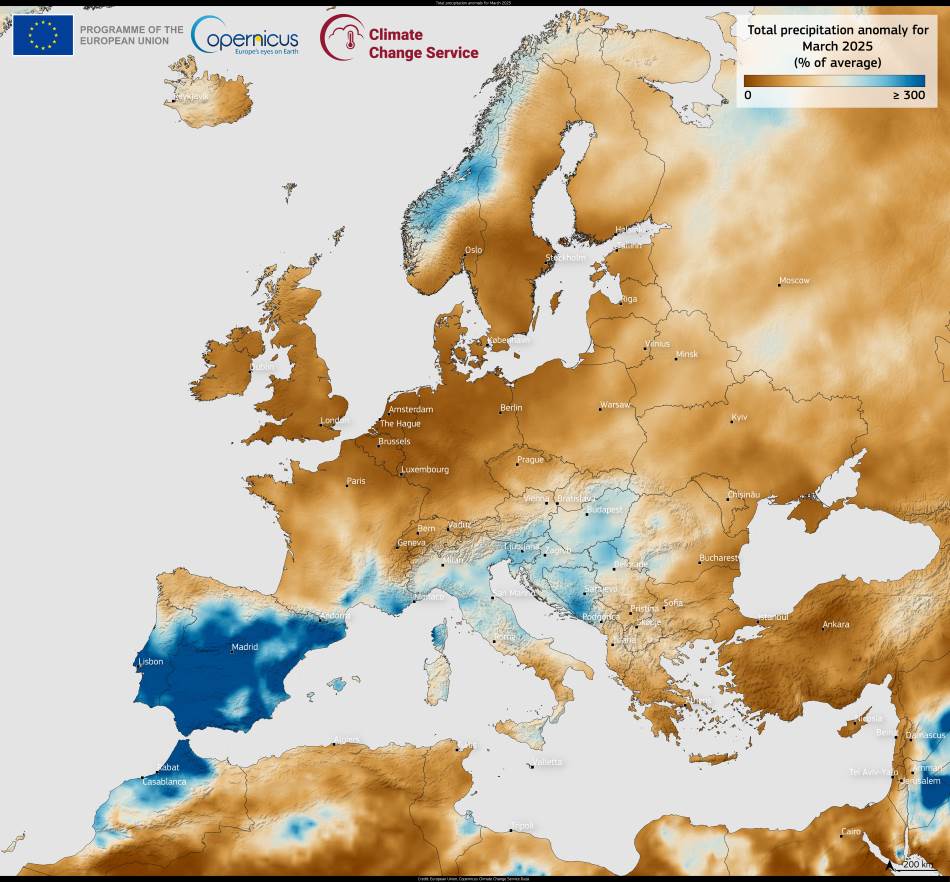
In contrast, the UK, Ireland, and a belt of countries extending from central Europe to the Black Sea, including Greece and Türkiye, recorded drier-than-usual conditions. Rainfall levels in these regions fell below the long-term March average, raising concerns about low soil moisture and the potential for early-season drought in agricultural zones. The dryness follows a broader trend observed in recent months in some of these areas.
The Copernicus map shows anomalies relative to the 1991–2020 climatological reference period, providing a monthly snapshot of changing rainfall patterns. These patterns are important for understanding how atmospheric dynamics are evolving across Europe. Variability from one region to another, as seen in March, can have significant implications for water resources, agriculture, and flood risk.
C3S makes its climate monitoring data openly available to support planning and policy development. Monthly bulletins like this one play a key role in tracking the state of the climate, helping governments, researchers, and the public stay informed about changing environmental conditions.
Featured image credit: European Union, Copernicus Climate Change Service Data



