Paris, France | AFP
Our ancestor Homo erectus was able to survive punishingly hot and dry desert more than a million years ago, according to a new study that casts doubt on the idea that Homo sapiens were the first humans capable of living in such hostile terrain.
The moment when the first members of the extended human family called hominins adapted to life in desert or tropical forests marks “a turning point in the history of human survival and expansion in extreme environments,” lead study author Julio Mercader Florín of the University of Calgary told AFP.
Scientists have long thought that only Homo sapiens, who first appeared around 300,000 years ago, were capable of living sustainably in such inhospitable regions.
The first hominins to have split off from the other great apes were believed to be limited to less hostile ecosystems, such as forest, grasslands and wetlands.
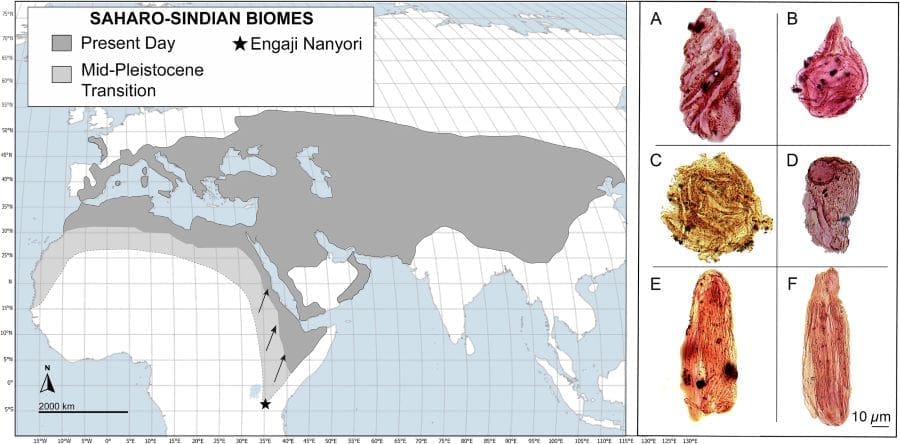
One of the world’s most important prehistoric sites, Olduvai Gorge in modern-day Tanzania, was thought to home to those easier types of landscapes.
But this steep ravine in East Africa’s Great Rift Valley, which has played a key role in the understanding of human evolution, was actually a desert steppe, according to the study published in the journal Communications Earth & Environment on Thursday.
After collecting archaeological, geological and palaeoclimatic data, the international team of researchers were able to reconstruct the gorge’s ecosystem over the years.
Fossilised pollen of the Ephedra shrub — which commonly lives in arid areas — as well as traces of past wildfires and signs in the soil show there was an extreme drought in the area between one and 1.2 million years ago.
Homo erectus: underestimated?
Evidence collected from the Engaji Nanyori site in the gorge suggests that Homo erectus adapted to this hostile environment “by focusing on ecological focal points such as river confluences where water and food resources were more predictable,” Mercader Florin said.
“Their ability to repeatedly exploit these focal points… and adapt their behaviours to extreme environments demonstrates a higher level of resilience and strategic planning than previously assumed.”
Specialised tools found at the site, such as hand axes, scrapers and cleavers, showed that Homo erectus had also worked out how to process animal carcasses.
The bones of animals such as cows, hippopotamuses, crocodiles and antelopes also had cut marks, indicating they had been skinned and had their bone marrow extracted.
“This suggests they optimised their resource use to adapt to the challenges of arid environments, where resources were scarce and needed to be exploited fully,” Mercader Florin said.
“Our findings show that Homo erectus was capable of surviving long term in extreme environments characterised by low density of food resources, navigational challenges, very low/very high plant life, temperature/humidity extremes, and the need for high mobility,” he added.
“This adaptability expands Homo erectus’s potential range into the Saharo-Sindian region across Africa and into similar environments in Asia.”
ber/dl/js
© Agence France-Presse
Journal Reference:
Mercader, J., Akuku, P., Boivin, N. et al. ‘Homo erectus adapted to steppe-desert climate extremes one million years ago’, Communications Earth & Environment 6, 1 (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s43247-024-01919-1
Note: Homo erectus, the first fully upright human species, emerged two million years ago. New dating reveals it survived on Java until just over 100,000 years ago, long after disappearing elsewhere. This surprising longevity means it coexisted with early Homo sapiens
Article Source:
Press Release/Material by Bénédicte Rey | AFP
Featured image credit: Freepik (AI gen)




