Berlin, Germany – CO2 emissions from road transport could peak worldwide this year thanks to rapid growth in electric vehicles and stricter new regulations, a German think tank said Tuesday.
The International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT) estimated that vehicle emissions would top out at around nine gigatonnes in 2025, a quarter-century earlier than previously predicted.
The volume of emissions would then decline to 7.1 gigatonnes in 2050, the ICCT calculated in a scenario based on environmental rules as of August 2024.
The organisation’s previous forecast, which used regulatory conditions in 2021, predicted a peak in road transport emissions in 2050.
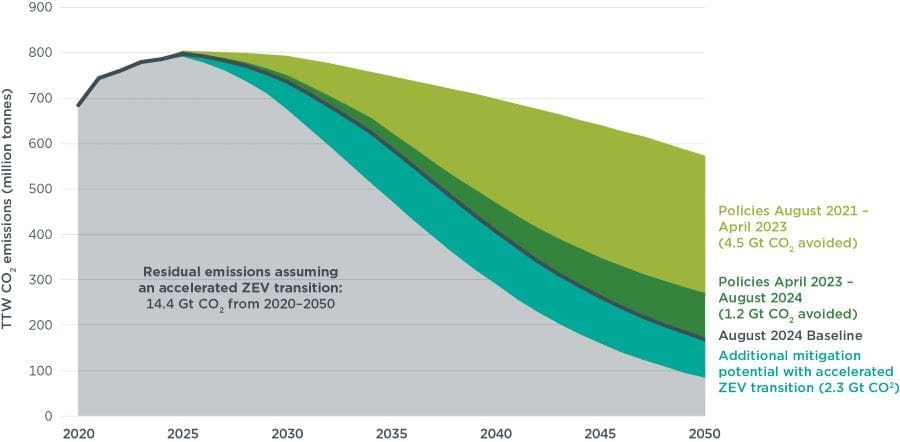
The quicker turnaround was due to changing regulations in major markets that required a higher share of zero-emissions vehicles (ZEVs), including battery-powered cars, in new sales, the ICCT said.
Progress in the number of cleaner vehicles already on the roads was “underpinned by the falling costs of ZEVs”, the ICCT said.
The think tank, however, warned that a weakening of current environmental standards for road transport could lead to the peak being delayed.
The European Union for example has agreed to ban the sale of new petrol and diesel cars from 2035 but criticism of the plan has grown.
The target is increasingly under fire from Europe’s struggling automotive industry and has become a bugbear of many far-right political parties in the bloc.
An increase in global vehicle activity or a slowdown in the sale of ZEVs could also delay the peak, the ICCT said.
While the difference between the two scenarios modelled by the think tank was already significant, yearly emissions would have to fall to 2.3 gigatonnes by 2050 to align with the Paris climate accords.
The climate deal set a target to limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels — and to 1.5C if possible.
The ICCT included all emissions linked to road transport in its modelling, including vehicle production and fuel use.
bur-fec-sea/fz/lth
© Agence France-Presse
More information:
Arijit Sen, Jacob Teter, and Josh Miller, ‘Vision 2050: Update on the global zero-emission vehicle transition in 2024’, The International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT), Jan. 2025.
Article Source:
Press Release/Material by AFP
Featured image credit: G.C. | Pixabay




