Conservation International and Sateri, a leading producer of manmade cellulose fibers, have launched the third phase of the Poyang Lake Ecosystem Restoration Initiative. This milestone marks five years of efforts to restore China’s largest freshwater lake, located in Jiangxi Province, while integrating climate resilience and carbon neutrality strategies.
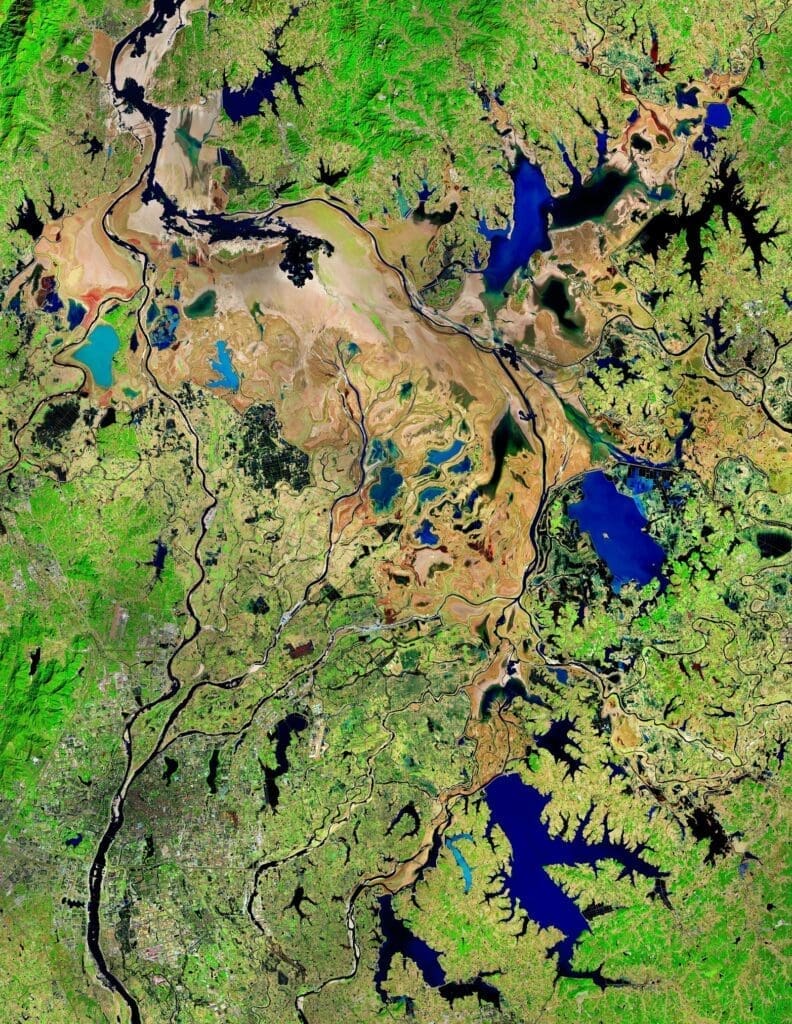
Poyang Lake, a vital waterbody in southeastern China, contributes over 15% of the Yangtze River’s annual runoff, supports 45 million residents, and provides critical habitats for endangered species, including the Siberian crane and Yangtze finless porpoise. The initiative, which began in 2019, has already made significant strides, including enhancing biodiversity, improving wetland management, and supporting local communities.

According to Zhang Cheng, Program Director at Conservation International China: “This initiative has truly enhanced biodiversity conservation and ecological education while empowering local communities with sustainable livelihoods. It demonstrates the value of collaborative approaches in balancing ecological protection with human well-being.”
Since its inception, the program has:
- Strengthened management across 473,000 hectares of protected areas.
- Enhanced the skills of 2,000 wetland rangers.
- Improved habitats for 350 species of wildlife.
- Constructed five artificial wetlands for wastewater treatment, managing 56,000 tonnes of sewage.
- Benefited 25,000 community members through education and livelihood programs.
The latest phase aims to deepen these impacts with a focus on research using the Freshwater Health Index (FHI), protecting small wetlands, and addressing climate change through mitigation and adaptation measures.
Addressing climate change and fostering collaboration
Supported by the Jiujiang Municipal Government, this initiative aligns with Sateri’s sustainability aspirations and the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. Cai Zhichao, Vice President of Operations at Sateri, highlighted the importance of integrating conservation into business practices: “At the heart of our operations lies a commitment to the bioeconomy, where we aim to protect the natural resources we use. This conservation initiative not only helps us meet our internal sustainability targets but also contributes to advancing At the heart of our operations lies a commitment to the bioeconomy, where we aim to protect the natural resources we use. This conservation initiative not only helps us meet our internal sustainability targets but also contributes to advancing the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UNSDGs)”, related to clean water, sustainable cities, and climate action.
The project also underlines the ecological significance of Poyang Lake, which expands to six times its size during flood seasons, providing essential ecosystem services such as flood control, water storage, and carbon sequestration. It serves as a wintering ground for migratory birds and a crucial habitat for 14 endangered waterfowl species, reinforcing its role in global biodiversity conservation.
As climate change threatens ecosystems and communities worldwide, the Poyang Lake initiative showcases how public-private partnerships can drive meaningful, scalable environmental action while supporting sustainable development.
Article Source:
Press Release/Material by Media OutReach via AFP
Featured image credit: Contains modified Copernicus Sentinel data (2016), processed by ©ESA | CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO