A study by researchers at Peking University’s Institute of Carbon Neutrality has unveiled how plants and animals respond differently to climate change in their seasonal biological cycles, or phenology. This large-scale analysis, led by Piao Shilong and Zhang Yao, highlights increasing mismatches between the two groups, raising concerns about the stability of ecosystems.
Published in Nature Ecology & Evolution, the study compiled an extensive dataset of phenological observations, including nearly half a million time series for plants (covering 1,629 species or genera across 248 events) and over 43,000 for animals, covering numerous species and events across four decades.
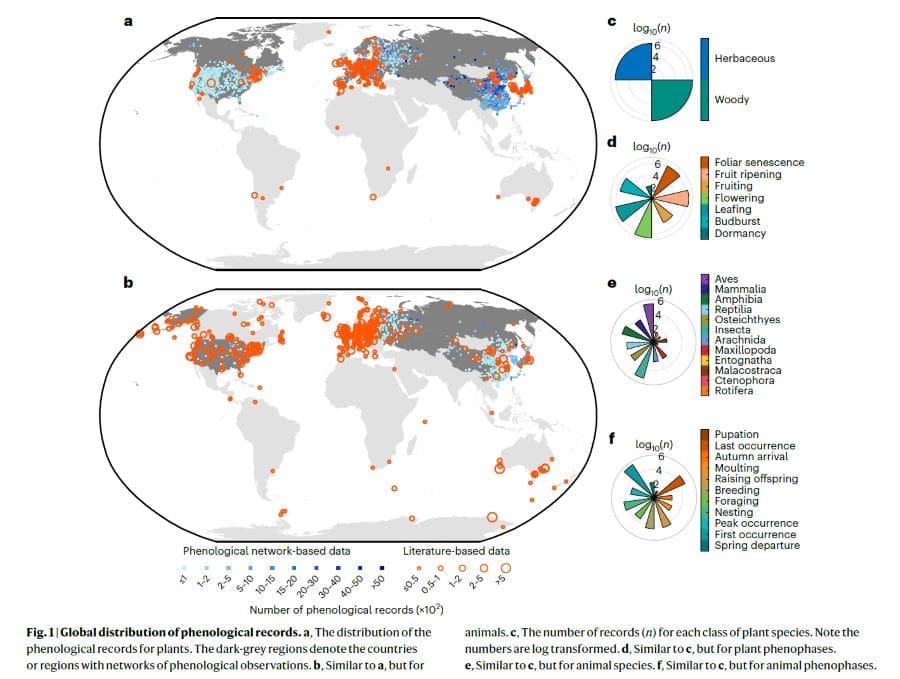
The findings show that plants exhibit a stronger response to warming, with later seasonal events such as fruiting advancing significantly over time. Nearly 30% of these changes were influenced by earlier events in the same growing season, suggesting that warming effects accumulate and amplify as seasons progress.
By contrast, animals displayed weaker and more variable phenological shifts. While insects showed slight advancements, the timing of seasonal activities in birds, mammals, and amphibians was often delayed. This variability stems from animals’ reliance on environmental cues, such as temperature or resource availability, which weakens the link between successive phenological events.
The research highlights that these divergent mechanisms may lead to increasing asynchrony between plants and animals. For instance, earlier flowering in plants might not align with the activity of pollinators, potentially disrupting trophic interactions. Such imbalances could ripple through ecosystems, affecting their overall functioning and stability.
The paper, co-authored by Lang Weiguang, Piao Shilong, and Zhang Yao, indicates the need to understand these phenological divergences to predict ecosystem responses to ongoing climate warming. The researchers emphasize that addressing such asynchrony is crucial to safeguarding ecological balance in a warming world.
Journal Reference:
Lang, W., Zhang, Y., Li, X. et al. ‘Phenological divergence between plants and animals under climate change’,Nature Ecology & Evolution (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41559-024-02597-0
Article Source:
Press Release/Material by Peking University
Featured image credit: kuritafsheen77 | Freepik




