Geologists have uncovered how tectonic forces shaped coastal mountain ranges in eastern Asia over 100 million years ago, triggering profound climate shifts during the Cretaceous period.
A study published in Science Advances reveals that the thickening of Earth’s crust along China’s eastern and southeastern coasts, driven by tectonic plate movement, created peaks soaring up to 2,500 meters. These changes altered global atmospheric patterns, intensified regional rainfall, and expanded inland deserts, shedding new light on the interplay between geology and climate during prehistoric times.
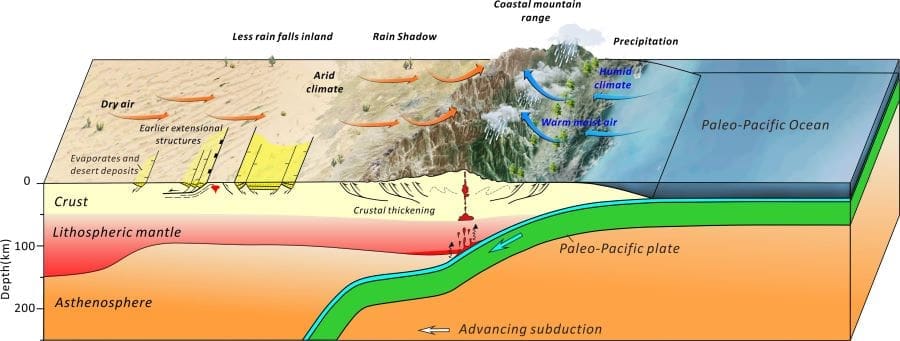
Monash University – Geologists have for the first time determined how coastal mountains in eastern Asia formed, resulting in significant changes to the continent’s climate more than 100 million years ago.
Until now, there were questions around the Asian climate during this time, commonly referred to as the Cretaceous period.
New research shows the sudden movement of tectonic plates that join beneath the continent about 120 million years ago resulted in the thickening of the Earth’s crust on the eastern and south-eastern coast of China, forming mountain ranges peaking at up to 2,500 m above sea level.
Peter Cawood, a Professor of geology in Monash University’s School of Earth, Atmosphere and Environment, collaborated with researchers in China and Canada to complete the research.
He said the findings set the scene for further research into the implications of climate change on evolution of plants and wildlife during the Cretaceous period.
“What we are able to learn from studying the formation of these mountain ranges is that it changed global atmospheric circulation patterns and increased rainfall in the area,” Professor Cawood said.
“Changes like this can affect the land significantly, and in this case we found inland aridity climbed by about 15 per cent, which saw the eastward expansion of the desert.
“So our research presents a more complete picture of the Earth at that time, which can then be applied to different aspects of plant and animal life, and later humans, to see the impact on evolution.
“This research presents a more complete picture of Earth at that time, filling significant gaps in our existing understanding of the climate during this period, and providing clues on how plant, animal and later human life evolved.”
The findings came from the analysis of hundreds of granite rocks from the region, aged between 160 and 80 million years, which can provide evidence of the conditions in the area at the time.
“This is a huge belt of hundreds of thousands of square kilometres of granitic rock, which has elemental ratios in part related to the thickness of the Earth’s crust,” Professor Cawood said.
“We can not only tell the age of rocks from the elemental composition, but the crustal thickness through time.
“We can then apply a climate model and check for various types of rock to gather information about the atmospheric conditions at that time.”
Journal Reference:
Jianhua Li et al. ‘Cretaceous coastal mountain building and potential impacts on climate change in East Asia’, Science Advances 10, eads0587 (2024). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.ads0587
Article Source:
Press Release/Material by Monash University
Featured image credit: Peter Cawood




