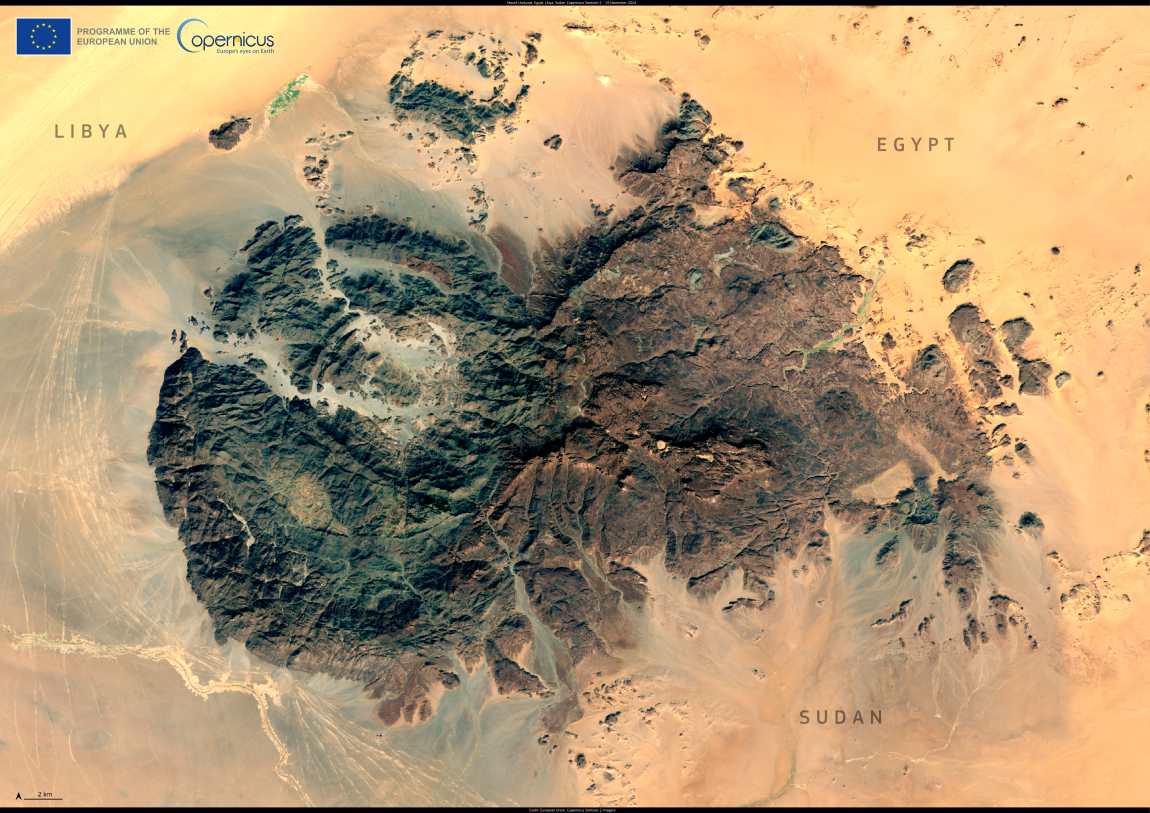
Rising dramatically from the heart of the Sahara Desert, Jebel Uweinat (Mount Uwaynat) stands as a monumental natural landmark where the borders of Egypt, Libya, and Sudan converge. This mountain massif, reaching an impressive height of nearly 2,000 meters, commands attention with its rugged peaks and stark beauty, offering a glimpse into both the geological and cultural history of the region.
Jebel Uweinat is renowned not only for its striking landscape but also for its prehistoric rock art. The ancient carvings and paintings scattered across its rocky surfaces depict animals and human figures, shedding light on a time when the now-arid Sahara supported abundant life. These artworks offer invaluable insights into the cultures and environments that thrived in this region thousands of years ago, long before the desert sands took over.
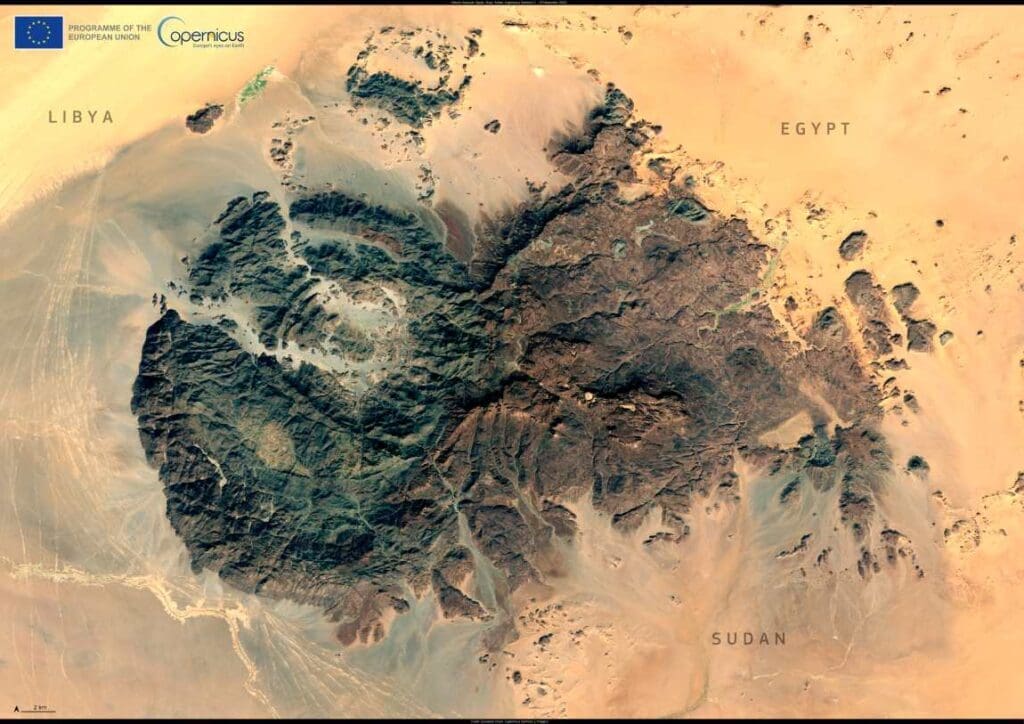
The mountain’s remote location in one of the harshest environments on Earth makes it a challenging destination, yet it remains an irresistible draw for adventurers, archaeologists, and scholars. Its significance extends beyond its towering height and archaeological treasures; it serves as a stark reminder of the Sahara’s complex and dynamic history.
Captured on 19 November 2024, this image from the Copernicus Sentinel-2 satellite provides a unique vantage point of Jebel Uweinat. The satellite’s data offers critical information about remote and inhospitable regions like this, enabling scientists and conservationists to monitor environmental changes. This capability is crucial for understanding the long-term impacts of climate change on fragile ecosystems and ancient cultural sites scattered across the desert.
Such satellite imagery highlights the interplay between natural beauty and human history, revealing landscapes that continue to inspire exploration while raising awareness about the importance of preserving these exceptional environments for future generations.
Featured image credit: European Union, Copernicus Sentinel-2 imagery