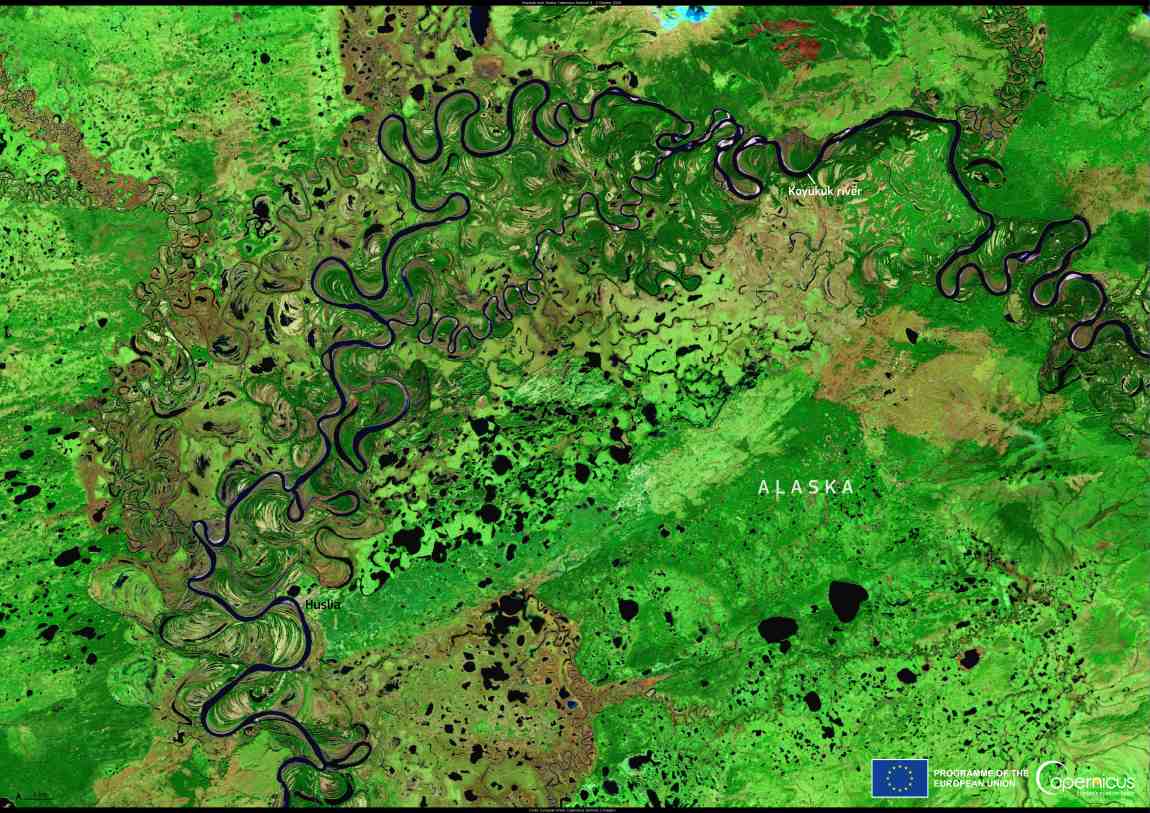
This image from the Copernicus Sentinel-2 satellite, acquired on 2 October 2024, shows part of the Koyukuk River in Alaska, USA. The area has been the subject of studies which have provided valuable insights into the Earth’s permafrost.
In Alaska, where many riverbanks are permanently frozen, mapping the extent of permafrost and analysing the vegetation helps researchers understand how permafrost responds to changes in air temperature.
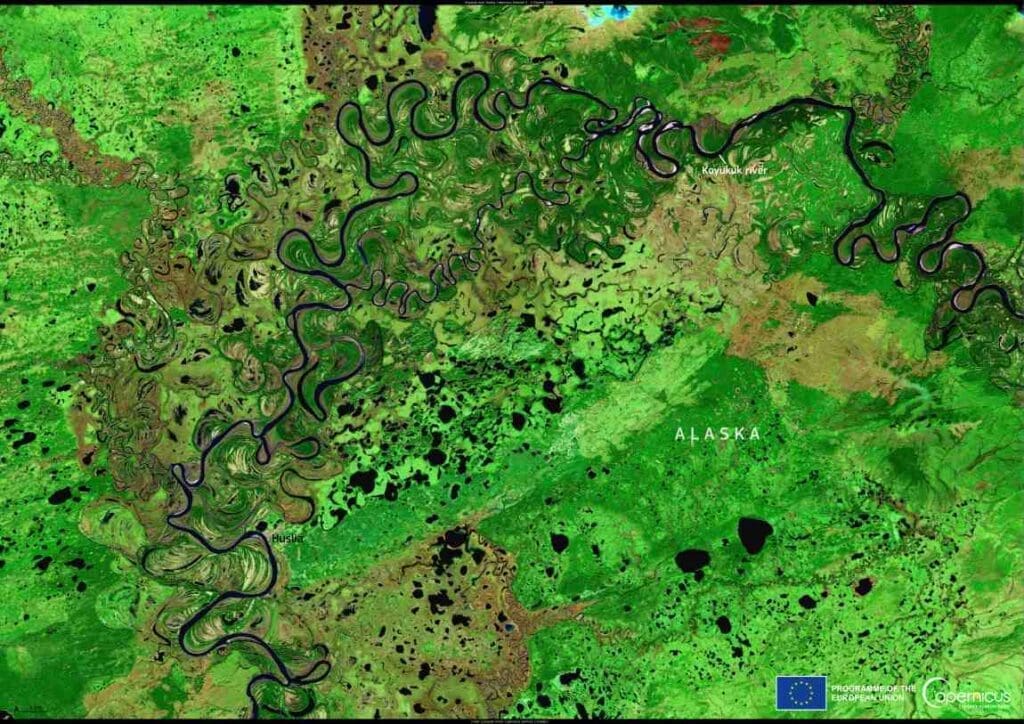
The findings show that new permafrost deposits are forming along the Koyukuk River. However, the rate of formation is not fast enough to counterbalance the thawing caused by rising temperatures. This is significant because melting permafrost releases carbon into the atmosphere, contributing to a warming climate.
The Copernicus Sentinel-2 satellites, equipped with multi-spectral instruments, play a key role in monitoring Earth’s bodies of water. The data they collect supports scientists and policymakers in understanding the impacts of climate change and developing strategies to address these challenges.
Featured image credit: European Union, Copernicus Sentinel-2 imagery