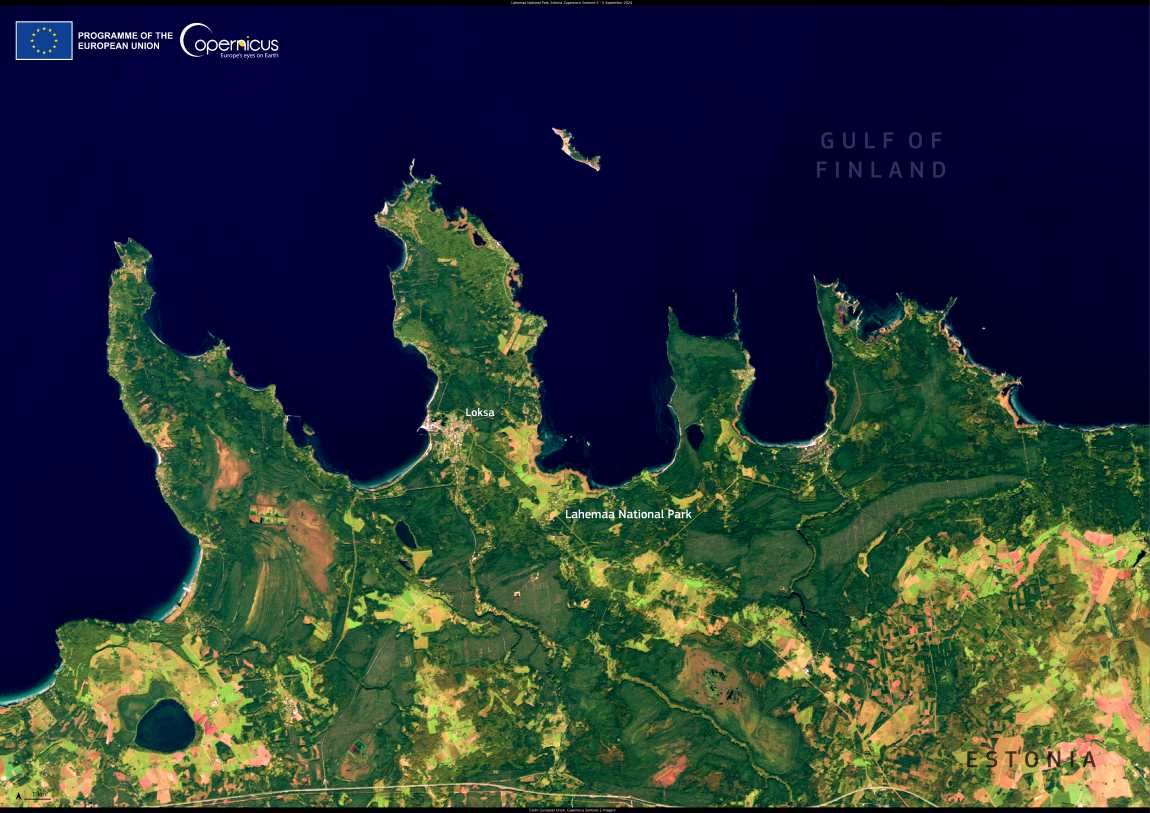
Lahemaa, located in northern Estonia on the southern shore of the Gulf of Finland, is the country’s oldest and largest national park, spanning over 725 km².
Established in 1971, it is renowned for its diverse ecosystems, including lush forests, wetlands, and beaches. A Natura 2000 site, the park is home to a variety of wildlife, such as moose, elk, and lynxes.
The park also hosts the highest deposit of erratic boulders in Europe thanks to glaciers which brought the boulders from Finland and Scandinavia to Estonia during the last Ice Age.
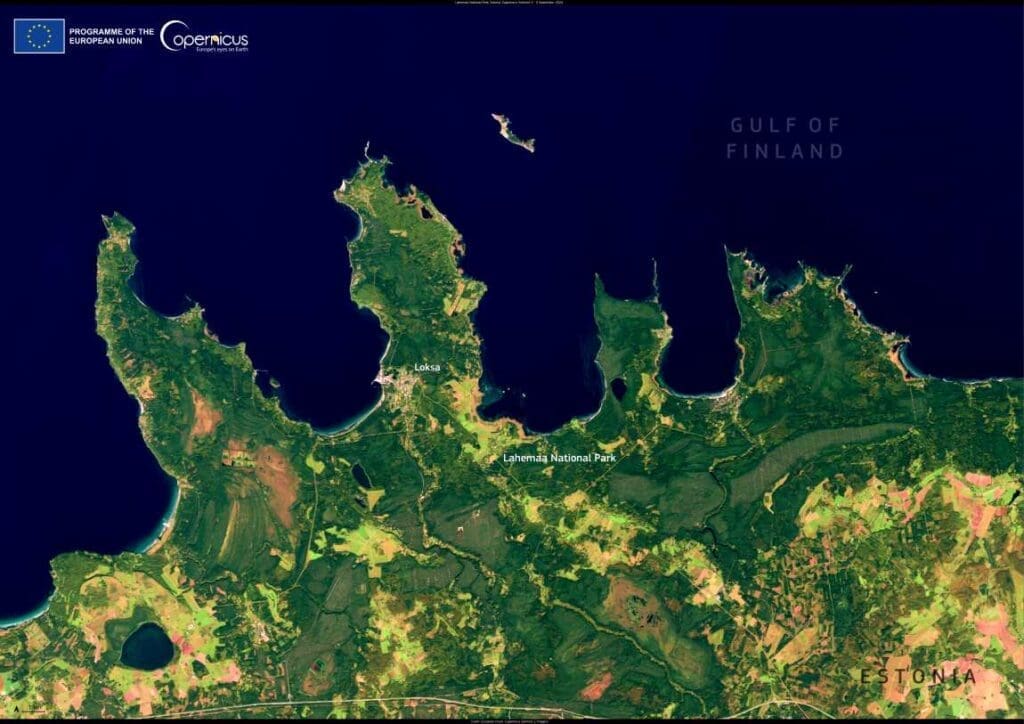
The park is shown in this image acquired by one of the Copernicus Sentinel-2 satellites on 5 September 2024.
Open data from the Copernicus Sentinel satellites helps to monitor essential ecosystems around the world, helping to ensure that their wildlife and unique environmental characteristics are well preserved.
Featured image credit: European Union, Copernicus Sentinel-2 imagery