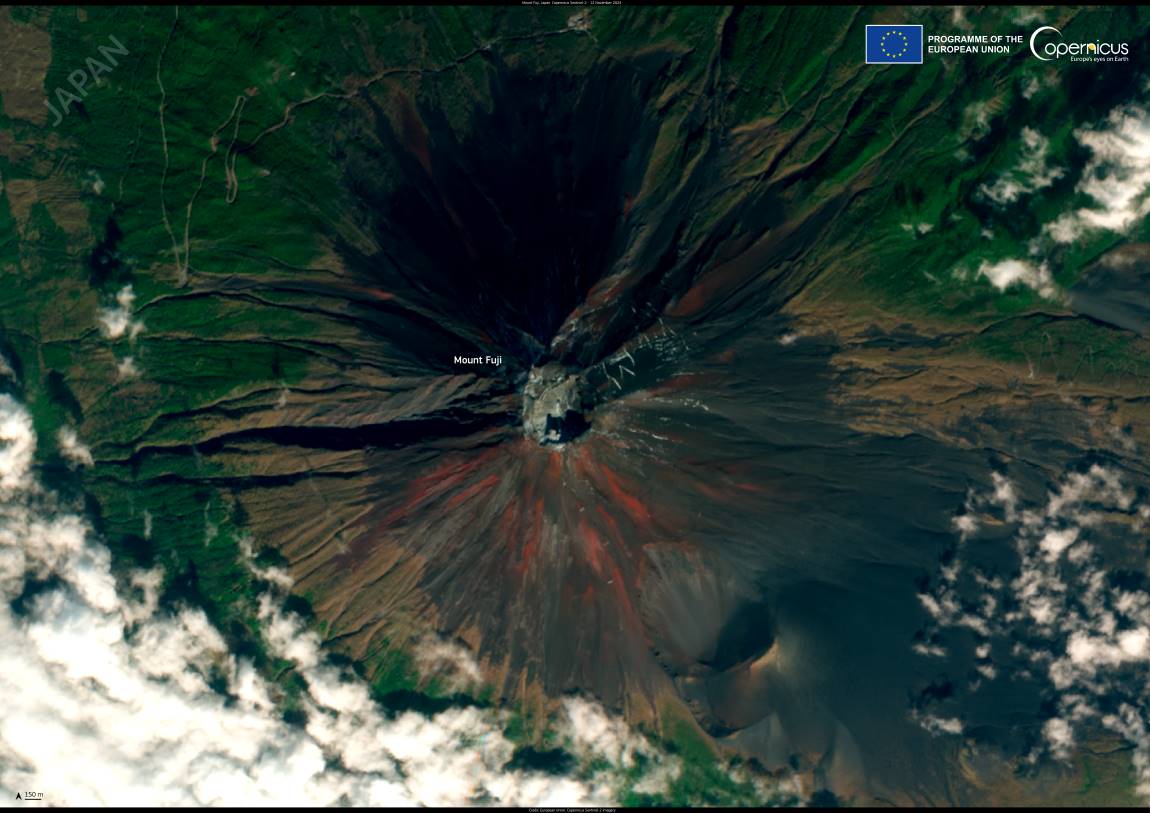
Mount Fuji, Japan’s renowned landmark and highest peak at 3,776 meters, has finally seen its first snowfall of the season, marking the end of an unprecedented snow-free period. This delay is notable not only for its length – 130 years since such records began – but also for the way it signals the shifting climate patterns impacting Japan and the broader region.
Typically, Mount Fuji would receive its first snowfall in early October. This year, however, the warmer-than-usual temperatures pushed the season’s first snow back until November, well after the peak summer heat.
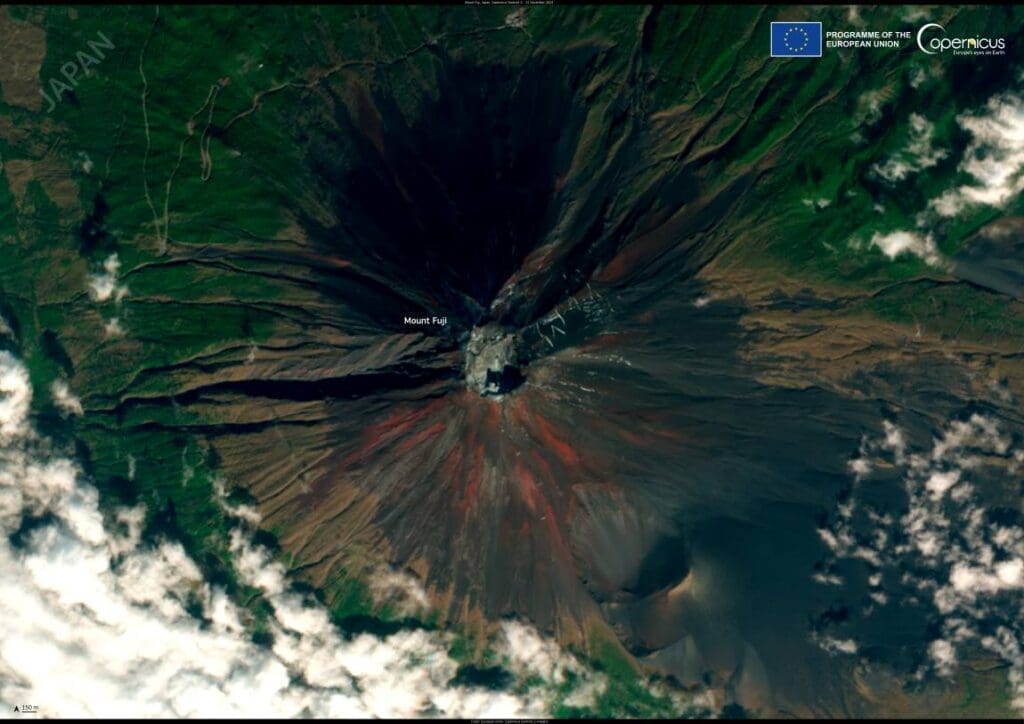
The delay follows Japan’s hottest summer on record in 2024, with temperatures from June to August soaring to 1.76°C above average. September and October also stayed warmer than average, continuing a trend that scientists link to the broader effects of climate change in Asia.
The accompanying Copernicus Sentinel-2 satellite image, captured on November 12, 2024, shows Mount Fuji with only faint white traces on its peak – an unusual sight for a mountain often capped in thick snow by this time of year.
The Copernicus Sentinel satellites, with their detailed imaging capabilities, are instrumental in documenting weather anomalies and climate data. The Sentinel images offer researchers vital insights into these shifting patterns, helping scientists make sense of climate trends with lasting implications for both local environments and global weather systems.
Featured image credit: European Union, Copernicus Sentinel-2 imagery