The Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) has published its latest monthly Climate Bulletin, focused on key climate trends in October 2024.
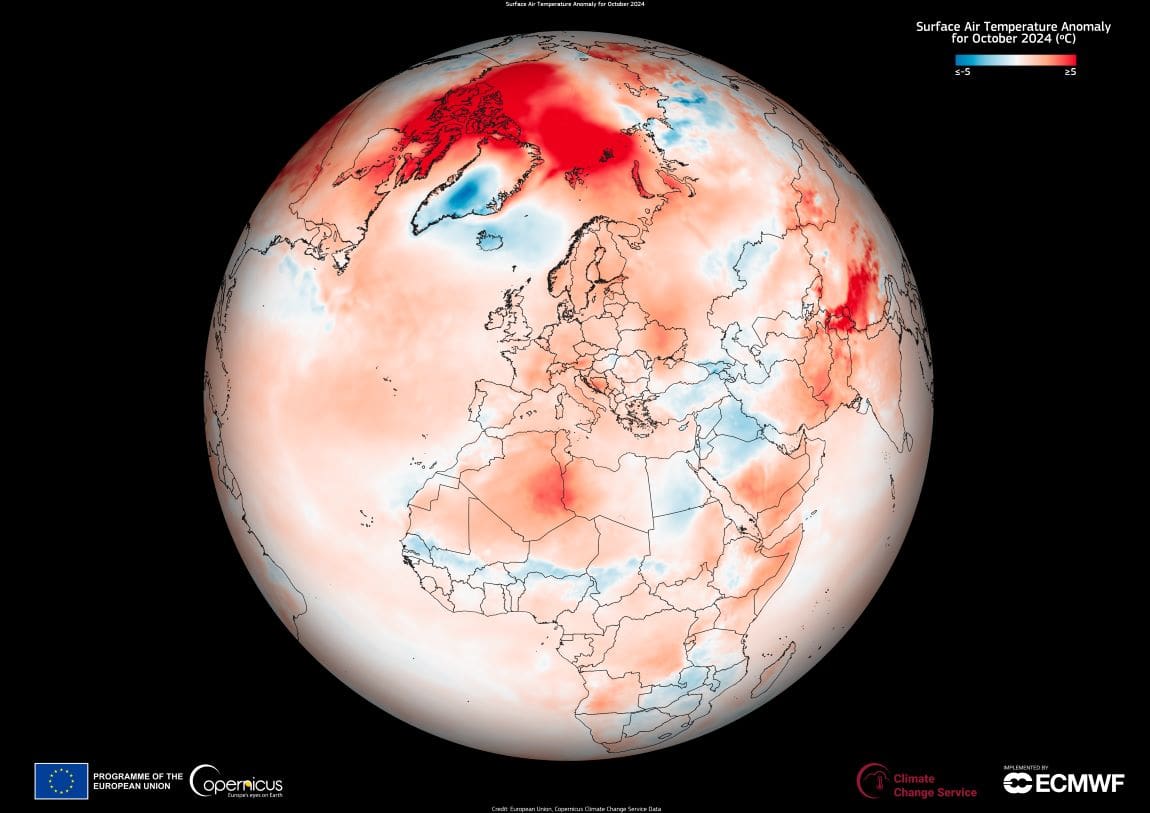
The bulletin reports that October 2024 was the second-warmest October on record globally, surpassed only by October 2023.
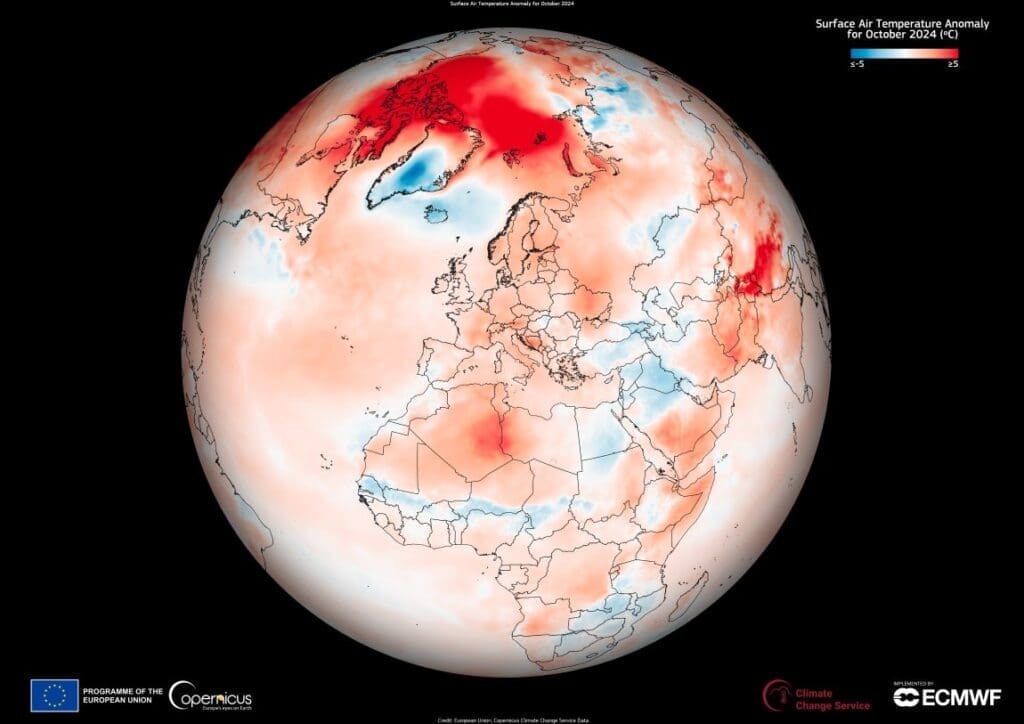
The month was 0.80°C warmer than the 1991-2020 October average, with an absolute surface air temperature of 15.25°C, and marked the fifteenth month within a 16-month period during which global average surface air temperatures exceeded 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels.
This data visualisation based on C3S data shows Europe, where October 2024 ranked as the fifth-warmest October on record, with average temperatures 1.23°C above the 1991-2020 monthly average.
Data from C3S is essential for monitoring trends in the global climate, ultimately supporting decisionmakers in creating and implementing climate strategies for the future.

More information is available here.
Featured image credit: European Union, Copernicus Climate Change Service Data