A research team led by Dr. Alexandre Pereira Santos at Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich has introduced a pioneering model designed to improve how scientists understand and respond to the growing convergence of global crises.
These include climate disasters, pandemics, species extinction, and violent conflicts – interacting risks that pose increasingly complex challenges in the Anthropocene, the current era shaped by human activity.
“We know that these risks cause damages and losses, which may become even greater when hazards interact and multiply their impacts,” explains Pereira Santos from LMU’s Department of Geography. For instance, the COVID-19 pandemic not only threatened public health, but also drove widespread economic hardship, revealing how multiple risks can exacerbate one another. Yet, the complexity of these interactions remains poorly understood, often eluding effective policy responses.
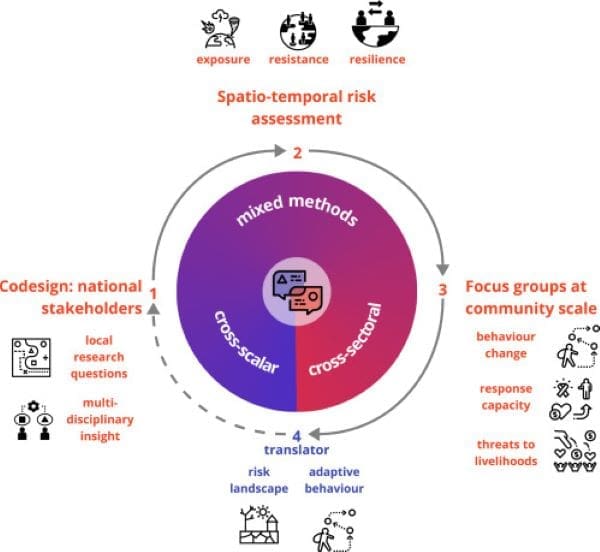
In a study recently published in One Earth, Pereira Santos and colleagues from Universität Hamburg and the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) introduce a new framework that aims to bridge the gap.
Their approach connects climate and social science perspectives using a “translator” model. This innovative tool allows researchers to consider diverse factors and scales, without losing the richness of the data, which is crucial for crafting more inclusive and context-aware policies.
“Before our approach, researchers often had to choose which aspects to consider in order to avoid information overload. Or they had to perform general analyses of multiple risks, regions, or social sectors, resulting in the loss of information,” says Pereira Santos. The new model resolves this issue by combining different sources of evidence into a coherent whole, preserving both the depth and breadth needed for comprehensive risk analysis.
This integrated method holds promise for shaping future policies that more effectively address the cascading impacts of crises, helping societies prepare for an increasingly interconnected world.
Journal Reference:
Alexandre Pereira Santos et al. ‘Integrating broad and deep multiple-stressor research: A framework for translating across scales and disciplines’, One Earth 7 (10), 1713 – 1726 (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.oneear.2024.09.006
Article Source:
Press Release/Material by Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (LMU)
Featured image credit: Freepik




