Starkville, Mississippi – Mississippi State University is part of a European-American collaboration studying how human activities, like fertilizer use and polluting, are impacting nitrogen-fixing plants which are crucial for maintaining healthy ecosystems by adding nitrogen to the soil.
MSU Assistant Professor Ryan A. Folk of the Department of Biological Sciences co-authored a study published in Science Advances, showing that increased nitrogen deposition from human activity is reducing the diversity and evolutionary distinctiveness of nitrogen-fixing plants.
Lead author of the study Pablo Moreno García, at the University of Arizona, said excessive nitrogen from agriculture and industry makes nitrogen fixers less competitive, leading to simplified plant communities with fewer species of nitrogen fixers.
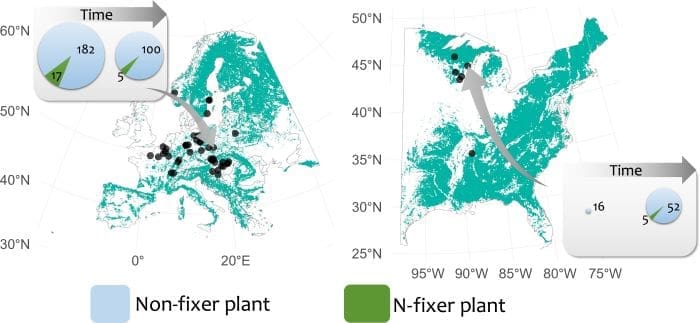
Folk said: “While others predicted climate change might benefit nitrogen fixers, our research shows this has not happened. Humans are changing Earth in multiple ways that affect nitrogen fixers, and nitrogen deposition is overwhelming as a harmful effect. Nitrogen, the first number listed on a bag of fertilizer, is often the most important plant macronutrient in natural and agricultural systems, so the loss of these plants threatens both biodiversity and ecosystem stability.”
Journal Reference:
Pablo Moreno-García et al. ‘Long-term nitrogen deposition reduces the diversity of nitrogen-fixing plants’, Science Advances 10, eadp7953 (2024). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adp7953
Article Source:
Press Release/Material by Mississippi State University
Featured image: Lathyrus palustris or marsh pea Credit: Elchin Guliyev | Unsplash



