Researchers at ETH Zurich have developed a novel technique to break down perfluorooctane sulfonates (PFOS), a subgroup of the hazardous “forever chemicals“ known as PFAS, using piezocatalysis. This innovative process employs nanoparticles and ultrasound to dismantle the resilient PFOS molecules, a development that could revolutionize existing water treatment methods.
Key Points:
- Piezocatalysis: A new technique using nanoparticles and ultrasound to break down PFOS molecules.
- Laboratory success: ETH Zurich’s research degraded 90.5% of PFOS in high-concentration water samples.
- Challenges ahead: Scaling up the process for real-world applications remains a hurdle.
PFAS, or per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, are synthetic chemicals found in products like firefighting foam, non-stick cookware, and water-repellent textiles. These chemicals persist in the environment, contaminating soil and water, and are linked to severe health risks, including cancer and liver damage.
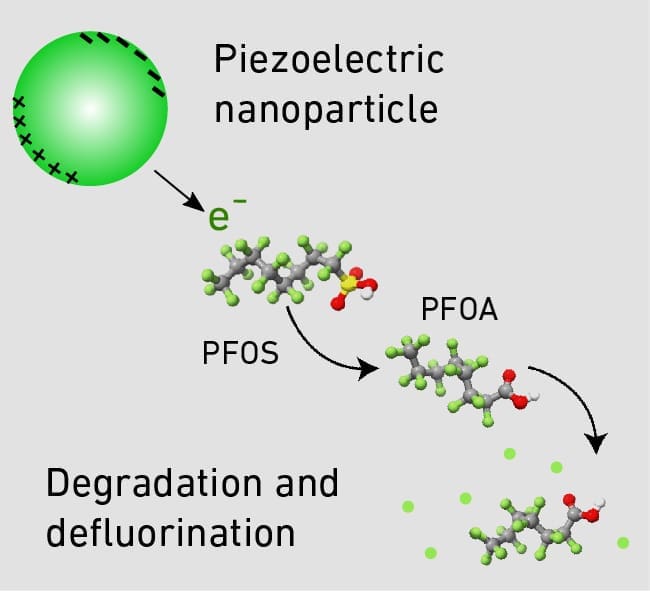
Breakthrough with piezocatalysis
The research team, led by Professor Salvador Pané i Vidal at ETH Zurich’s Institute of Robotics and Intelligent Systems, focused on PFOS, a particularly toxic form of PFAS. Despite restrictions on PFOS, it remains a contaminant in many environments due to its incredibly stable chemical structure.
Andrea Veciana, a doctoral student on the team, explained: “The molecules consist of long carbon chains surrounded by fluorine atoms. This carbon-fluorine bond is so strong that you need a lot of energy to break it.”
Using piezocatalysis, the researchers were able to overcome this challenge. This process relies on piezoelectric nanomaterials that generate an electrical charge when subjected to mechanical stress, such as ultrasound. These charged nanoparticles act as a catalyst, initiating a reaction that degrades the PFOS molecules in water.
“We’ve developed nanomaterials that are piezoelectric. To the naked eye, this material looks a bit like sand,” Veciana said.
In tests, the team degraded 90.5% of PFOS molecules in water, using concentrations of 4 milligrams per liter. However, in natural settings, PFOS concentrations are much lower, posing additional challenges.
A greener alternative to existing methods
Current methods for breaking down PFAS are energy-intensive or shift the problem elsewhere. For instance, thermal decomposition requires temperatures above 1,000 °C, while photocatalysis, which uses light, faces limitations in wastewater due to low light penetration. Absorption methods, meanwhile, merely collect PFAS without degrading them, necessitating further disposal solutions.
Piezocatalysis offers a potentially more efficient and scalable solution, as it can work with existing mechanical energy sources like turbulence in wastewater treatment plants.
“If water has to be purified in wastewater treatment plants and there’s already turbulence in the water, that energy could perhaps be harnessed to break down the PFAS in it,” Veciana noted.
The path ahead
Despite laboratory success, the scalability of the piezocatalysis method remains a significant obstacle.
“The scalability of our method is one of the biggest challenges,” Pané i Vidal admitted, though he emphasized the potential for broader application beyond PFOS, extending to other PFAS and micropollutants.
The researchers highlighted the importance of preventing PFAS contamination at the source, such as in industrial and agricultural wastewater treatment plants, before these chemicals reach the environment.
“Companies should take all possible measures to ensure that the water they release into the environment is as clean as possible,” Pané i Vidal stated.
Veciana underscored the importance of policy changes and increased transparency around the use of PFAS: “PFAS are a global problem that should be tackled first and foremost through policy change and more transparency.”
While regulatory measures are critical, innovation in PFAS degradation techniques like piezocatalysis remains essential to addressing the existing contamination of soil and water by these persistent chemicals.
Journal Reference:
Veciana A, Steiner S, Tang Q, Pustovalov V, Llacer-Wintle J, Wu J, Chen X, Manyiwa T, Ultra Jr. V, Garcia-Cirera B, Puigmartí-Luis J, Franco C, Janssen D, Nyström L, Boulos S, Pané S,‘Breaking the Perfluorooctane Sulfonate Chain: Piezocatalytic Decomposition of PFOS Using BaTiO3 Nanoparticles’, Small Science 2400337 (2024). DOI: 10.1002/smsc.202400337
Article Source:
Press Release/Material by ETH Zurich
Featured image credit: Freepik




