Stockholm University researchers have unveiled an alternative approach to assessing global water scarcity, revealing that the risks to water supply are more significant than previously understood.
Published in Nature Water, the study suggests that evaluating the environmental and governance conditions in regions where rain originates, rather than just where it falls, leads to a nearly 50% increase in the estimated risk to global water security.
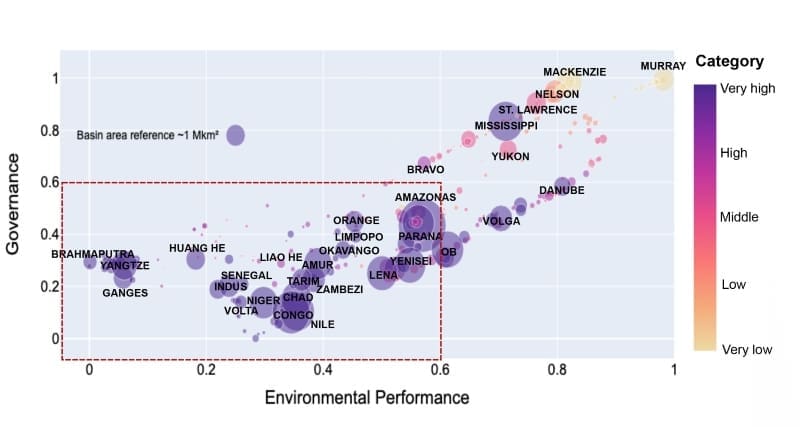
Traditionally, water security assessments focus on the rain that falls on the Earth’s surface and is stored in aquifers, lakes, and rivers. However, this new research emphasizes the importance of considering the source of the moisture that eventually becomes rain – a concept referred to as the precipitationshed. This approach takes into account the upwind regions where moisture evaporates from land or oceans before traveling through the atmosphere and falling as rain in downwind areas.
“Water supply really originates beforehand, with moisture evaporated from land or in the ocean traveling in the atmosphere before falling as rain. This upwind moisture is commonly overlooked when assessing water availability,” explained Fernando Jaramillo, associate professor in physical geography at Stockholm University and the study‘s lead researcher.
By analyzing 379 hydrological basins around the world, the researchers found that when the upwind origin of water is considered, the volume of water facing very high risk increases from 20,500 km³ per year to 32,900 km³ per year.
The study also highlights the significant impact that political and environmental management in upwind regions can have on downwind water security.
For example, deforestation and agricultural development in upwind areas can reduce the amount of moisture available for downwind rainfall, thereby increasing the risk of water scarcity. This is particularly concerning for landlocked countries like Niger, which rely heavily on moisture evaporated from neighboring countries such as Nigeria and Ghana.
Lan Wang-Erlandsson, a co-author of the study from the Stockholm Resilience Centre, emphasized the interdependence between upwind and downwind regions: “It is not possible to ignore the interdependence between countries. In the end, all water is connected, so we should not only mind how we manage our water resources within a region or country but also how our neighboring countries do.”
The study underscores the need for international cooperation in managing upwind moisture sources, suggesting that a shift in perspective could help mitigate water-related tensions and improve global water governance frameworks.
Journal Reference:
Posada-Marín, J., Salazar, J., Rulli, M.C. et al. ‘Upwind moisture supply increases risk to water security’, Nature Water (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s44221-024-00291-w
Article Source:
Press Release/Material by Stockholm University
Featured image credit: jcomp | Freepik




