New paper provides essential framework for evaluating the feasibility, impacts, and governance of stratospheric aerosol injection as a potential climate solution.
In a world increasingly grappling with the impacts of climate change, scientists are exploring innovative strategies to cool the planet. One of the most discussed methods is Stratospheric Aerosol Injection (SAI), which involves injecting sulfur dioxide into the stratosphere to reflect sunlight and reduce global temperatures. This approach is not without its complexities and risks.
To address these concerns, an international team of scientists led by the U.S. National Science Foundation National Center for Atmospheric Research (NSF NCAR) has released a new paper outlining critical guidelines for assessing the viability and impacts of SAI.
The article, published in Oxford Open Climate Change, provides a comprehensive framework for evaluating SAI proposals, with the aim of ensuring that any research or potential deployment is both scientifically sound and socially responsible.
A critical assessment framework
The paper emphasizes the need for a detailed evaluation of SAI, focusing on its technical feasibility, potential cooling benefits, and possible ecological and societal side effects.
“The goal is to work toward an assessment that can be used to identify the most feasible and legitimate scenarios, based on both how much they reduce natural and societal risks as well as any unwanted side effects,” said Simone Tilmes, the lead author and a scientist at NSF NCAR. “If society were to ever consider implementing SAI, it is imperative that we provide the best possible scientific understanding to policymakers and the public.”
SAI draws inspiration from natural phenomena like volcanic eruptions, which release sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere, leading to a temporary cooling effect. However, the method’s potential to alter global climate patterns and impact ecosystems has prompted the need for rigorous research and governance.
Eight essential research criteria
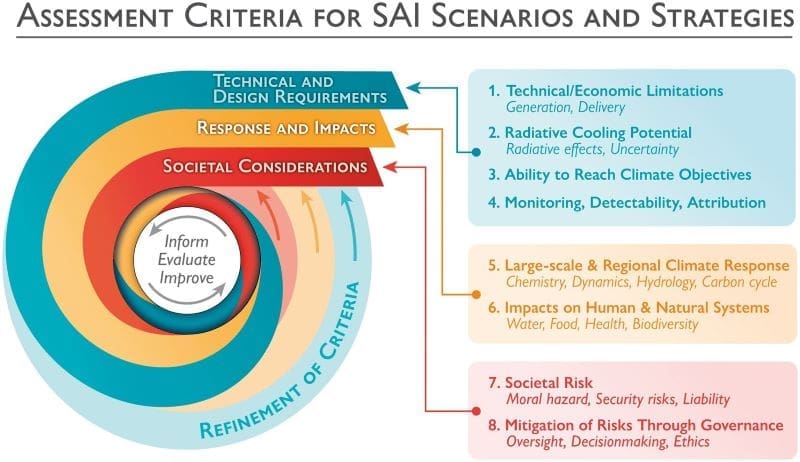
The paper proposes eight research criteria to guide future SAI studies:
- Technical and economic limitations: Assessing the practicality and costs of SAI technology.
- Cooling potential: Determining the extent to which SAI can lower global temperatures.
- Ability to meet climate objectives: Evaluating how well SAI aligns with global climate goals.
- Infrastructure for monitoring, detection, and attribution: Ensuring robust systems to track and measure SAI effects.
- Large-scale and regional climate response: Understanding the broader impacts on weather patterns and ecosystems.
- Impacts on human and natural systems: Analyzing how SAI might affect human health, agriculture, and biodiversity.
- Societal risks: Identifying potential social, political, and ethical challenges.
- Mitigation of risks through governance: Developing strategies to manage and mitigate risks, with input from global stakeholders.
These criteria are designed to ensure that SAI research is comprehensive and considers the perspectives of underrepresented communities, particularly those in the Global South who may be disproportionately affected by climate interventions.
Call for regular assessments
The authors recommend regular global assessments of SAI developments, conducted every few years, to keep pace with advancements in the field and evolving societal needs. “It’s time for such an assessment to occur, covering the criteria described in this paper, and repeated on a regular basis,” said Karen Rosenlof, a NOAA scientist and co-author of the paper. These assessments would provide a crucial resource for policymakers and the public, offering a transparent and up-to-date evaluation of SAI’s potential and risks.
A path forward
As the climate crisis intensifies, the need for innovative solutions like SAI becomes more urgent. However, the risks associated with such interventions necessitate careful, interdisciplinary research. By establishing these guidelines, the authors aim to pave the way for responsible and informed decision-making in the field of solar geoengineering.
“The goal of these criteria is to promote optimal approaches from a climate perspective while carefully weighing the benefits and risks and making sure to include the perspectives of underrepresented groups and the Global South,” Tilmes concluded.
This paper represents a significant step toward a structured, globally inclusive approach to solar geoengineering research, ensuring that any future interventions are conducted with the highest scientific and ethical standards.
Journal Reference:
Simone Tilmes, Karen H Rosenlof, Daniele Visioni et al., ‘Research criteria towards an interdisciplinary Stratospheric Aerosol Intervention assessment’, Oxford Open Climate Change 4, (1): kgae010 (2024). DOI: 10.1093/oxfclm/kgae010
Article Source:
Press Release/Material by NCAR/UCAR
Featured image credit: Freepik




