By Zhang Nannan | Chinese Academy of Sciences
In a study published in One Earth, a research team led by Prof. Deng Ye from Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences of the Chinese Academy of Sciences proposed the core-bacteria-forecast model (CoBacFM), which linked the changes of bacterial species, soil pH, and climate change together in global grassland ecosystem.
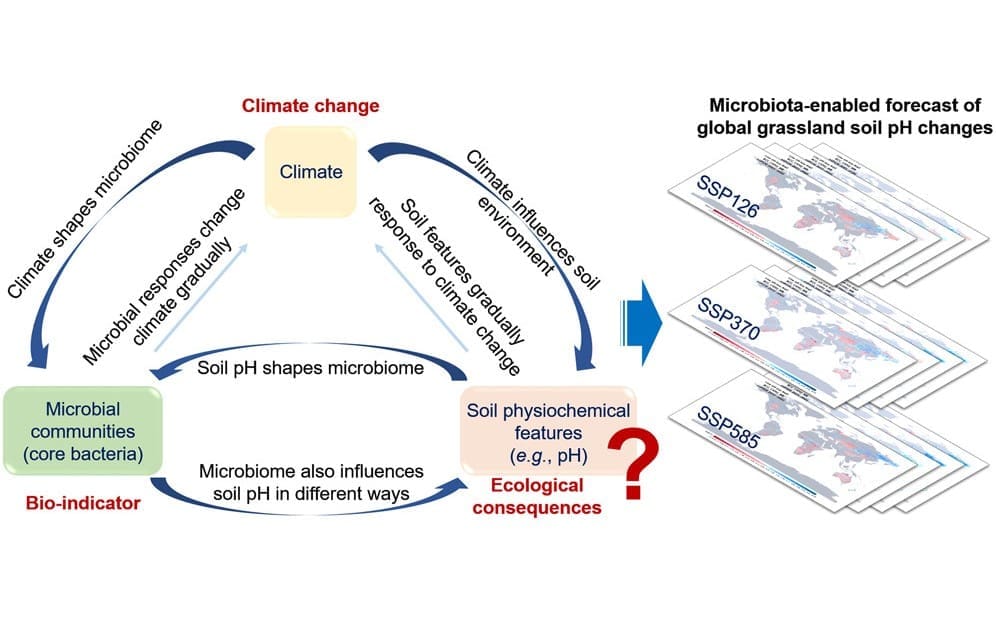
Soil microbiota are sensitive to climate change, and are key drivers of biogeochemical processes, particularly interacting with soil pH. However, current terrestrial models often neglect microbial communities due to their complexity and high diversity.
In this study, Deng and the international collaborators, including 12 research teams from 6 countries, expended extensive time gathering and construct the global grassland soil microbiota dataset.
“The co-authors are very willing to share their raw research data. This is very helpful in expanding the dataset”, said Prof. Deng, corresponding author of the study.
They found that the grassland soil pH changes under climate change can be well predicted through microbial responses.
Grassland soil pH tends to increase in Northeast Asia, Afirca, and Oceania, and decrease in Central North America, Southern Africa, and Eastern Asia. About one-third of the alkaline areas will become more alkaline. And the warming simulation field experiments support these predictions.
“This study shows that bacterial responses can serve as bioindicators of soil pH changes, providing valuable insights for future climate adaptation strategies. The model could be expanded to other ecosystems,” said Prof. Deng.
More information: Kai Feng, Shang Wang, Qing He, Yunfeng Yang, Jizhong Zhou, Ye Deng et al., ‘CoBacFM: Core bacteria forecast model for global grassland pH dynamics under future climate warming scenarios’, One Earth (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.oneear.2024.06.002. CAS Press Release / Material. Featured image credit: Charles MingZ | Unsplash




