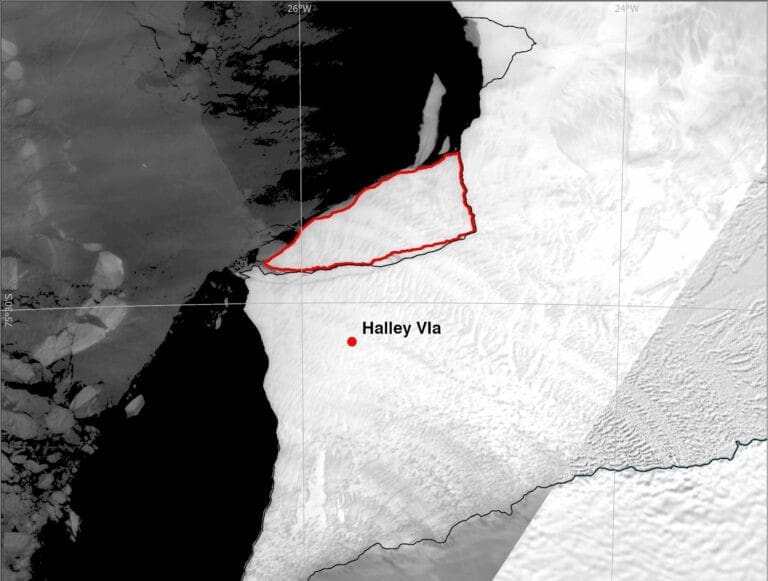
A large iceberg (380 km²), about the size of the Isle of Wight, has broken off the 150m thick Brunt Ice Shelf. It broke off after a crack suddenly appeared in the ice shelf a few weeks ago. The final break happened in the early hours of Monday 20 May.
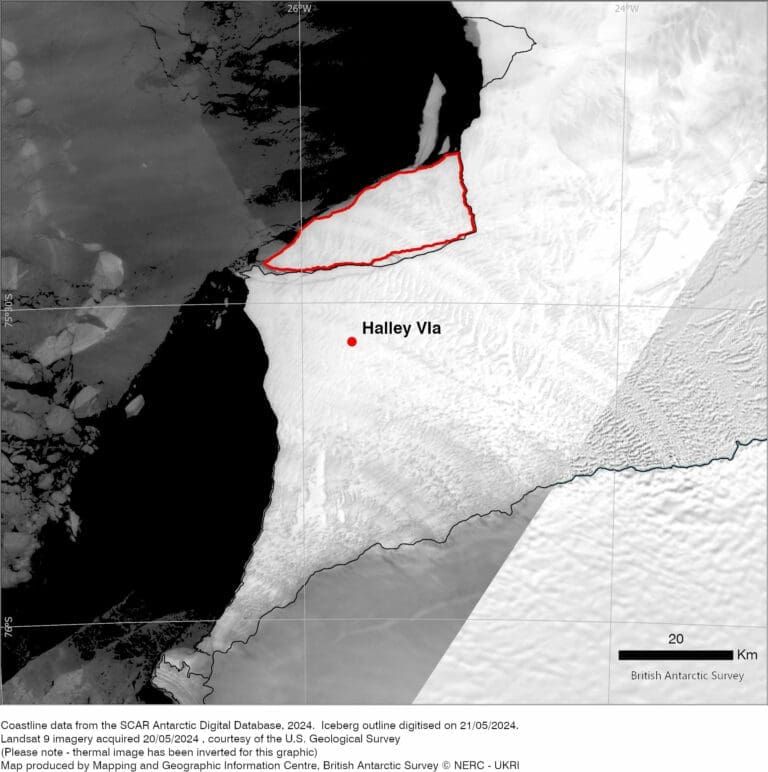
The iceberg calved after a 14km-long chasm formed at ninety degrees to the existing Halloween Crack. This follows a long period of weakening of the ice at the McDonald Ice Rumples. The break off is the third major iceberg calving from this area in the last four years and has taken place around a decade after scientists at British Antarctic Survey (BAS) first detected growth of vast cracks in the ice.
The calvings are not thought to be linked to climate change.
The Brunt Ice Shelf is the location of the British Antarctic Survey’s Halley Research Station. BAS glaciologists, who have been monitoring the behaviour of the ice shelf, say that the speed of the ice shelf where the research station is located has stabilised since the previous calving last year, and don’t expect a response to this new event.
In 2016, BAS took the precaution of relocating Halley Research Station 23 km inland of Chasm-1 after it began to widen.
Since 2017, staff have been deployed to the station only during the Antarctic summer (between November to March). Currently the station is unstaffed. A new team will return to Halley in November.
Dr Oliver Marsh, a glaciologist who has spent four seasons working on the Brunt Ice Shelf, first detected the calving from GPS equipment.
“This calving was expected since the appearance of Halloween Crack eight years ago and reduces the total area of the ice shelf to its smallest extent since monitoring began. “Tabular iceberg calving is part of the natural behaviour of ice shelves but often causes large changes in ice shelf geometry and can impact local ocean circulation. Our science and operational teams continue to monitor the ice shelf in real-time to ensure it is safe, and to maintain the delivery of the science we undertake at Halley”.
In the 2023-24 season, BAS scientists successfully collected ice cores and geophysical information from the ice shelf to help their modelling of the calving process as part of the RIFT-TIP project.
Professor Adrian Luckman, a professor at Swansea University studies Antarctic ice shelves. He says:
“Antarctica’s floating ice shelves grow gradually by ice flow and shrink episodically by iceberg calving. The balance between these two processes impacts their ability to hold back ice on land. It is concerning, therefore, that even in this relatively cold sector of Antarctica there have now been three large iceberg calvings in the last 3-4 years. The Brunt Ice Shelf is providing plenty of data to help us understand the calving process and predict the future evolution of these important ice bodies.”
Featured image credit: British Antarctic Survey | NERC | UKRI. BAS – Press Release