by Zhang Nannan, Chinese Academy of Sciences
The process of soil wind erosion is influenced by vegetation cover. From a functional point of view, vegetation can be divided into photosynthetic vegetation (PV) and non-photosynthetic vegetation (NPV). The NPV represents dormant and dead vegetation, crop residues, and litter, which are the main components of surface vegetation during the non-growing season. It also helps to reduce wind erosion during this time. However, the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) can generally reflect the fractional cover of PV, but it may not accurately reflect the fractional cover of NPV, leading to potential errors in estimating the fractional cover of NPV.
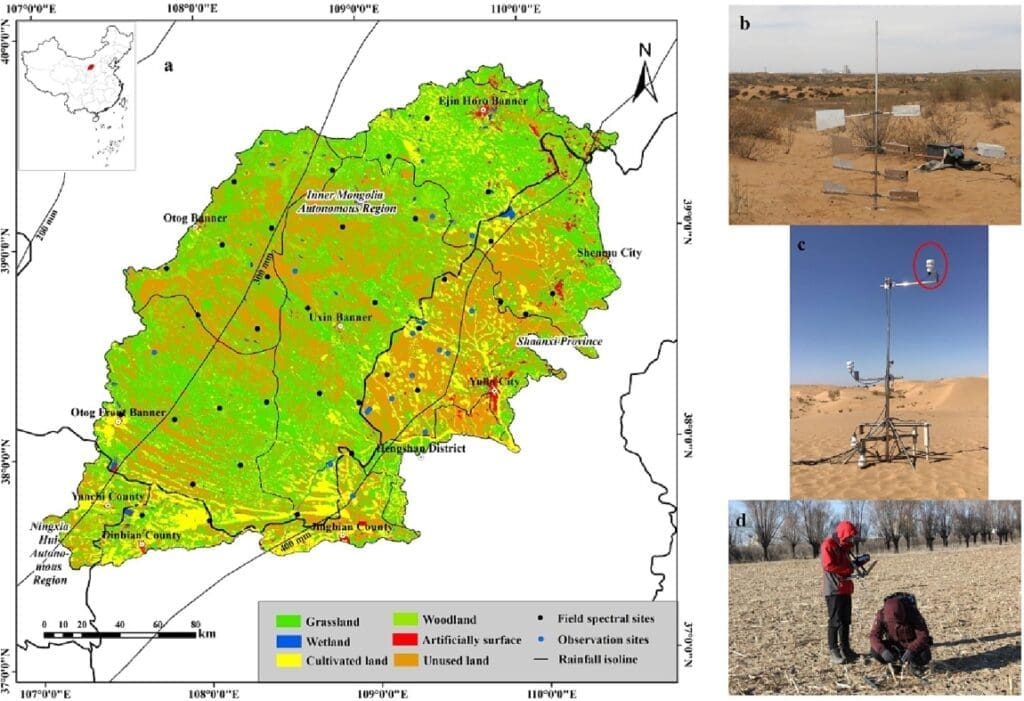
A research team from the Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources of the Chinese Academy of Sciences collected hyperspectral data on NPV to estimate the fractional coverage in the Mu Us Sandy Land (MUSL) using Landsat 8-OLI images from 2014 to 2017.
In the study published in Geoderma, the researchers conducted short-term observations of wind erosion to estimate the fractional cover of NPV and calibrate the simulated results to reduce uncertainties in wind erosion simulations.
They found that the mean values of NPV fractional cover in the MUSL from 2014 to 2017 were approximately 2.71 times higher than those estimated from NDVI data.
After coupling NPV into the revised wind erosion equation model, the simulation accuracy of this model obviously increased, which was validated by observational data.
Without considering NPV, the wind erosion modulus is overestimated. The wind erosion modulus was overestimated at rates of 130.48 t/km2/a, 91.79 t/km2/a, 85.51 t/km2/a, and 93.76 t/km2/a from 2014 to 2017, respectively. The corresponding wind erosion overestimation rates for these years were 26.52%, 16.9%, 21.47% and 31.33%, respectively.
In this study, NPV was integrated into the RWEQ model to enhance the simulation accuracy of this model and to provide a new perspective for the future development of wind erosion models.
This article is republished under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Read the original article.
(More information: Xiufan Liu et al, ‘An improvement of the Revised Wind Erosion Equation by considering the effect of non-photosynthetic vegetation’, Geoderma (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2024.116880)




