By Cazzy Medley | University of Maryland
April showers are increasingly becoming deluges due to climate change, and May flowers will never be the same.
And it’s not just April; the warming of the planet is causing a year-round, worldwide trend toward more intense but less frequent rainfalls, a dynamic that will increasingly impact plants worldwide, according to a University of Maryland-led study published this month in in Nature Reviews Earth & Environment.
Already in most regions, more than half of the total yearly rainfall occurs on the 12 wettest days of the year – a number likely to shrink as rainfall becomes more concentrated in fewer days.
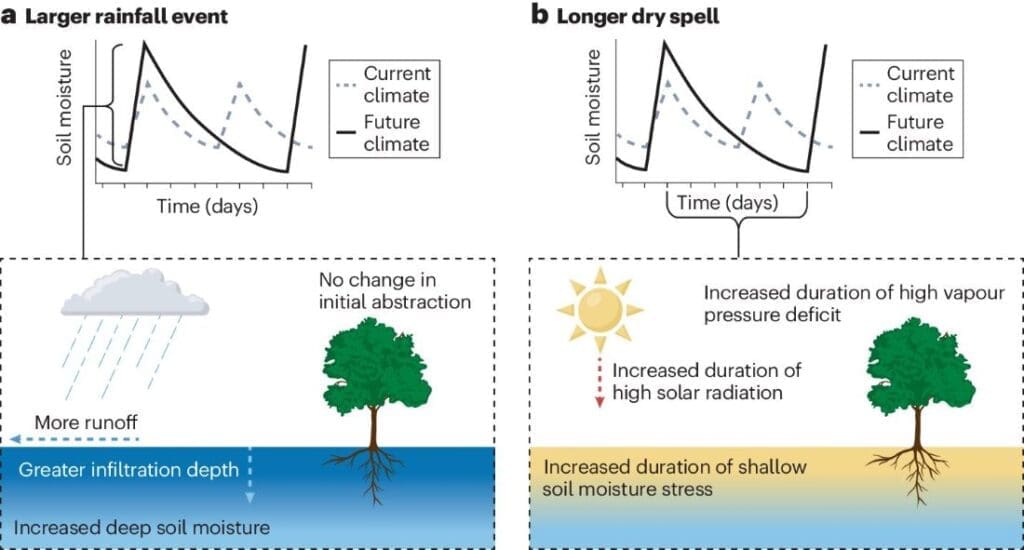
Longer dry periods interspersed with stronger downpours tend to benefit plants in dry places like the American West, while plants in wetter locations are burdened by these changes, according to a review by Earth System Science Interdisciplinary Center Researcher Andrew Feldman and colleagues that analyzed a broad range of previous studies using field experiments, satellite data and model simulations.
These contrasting responses can be attributed to how different plants respond to water, the researchers said. Dry ecosystem plants are more sensitive to large rainfall pulses compared with wet ecosystem plants, and thus benefit from downpours. However, plants within the same ecosystem can vary in how they respond to rainfall, meaning climate change has the potential to shift the plant composition of whole ecosystems.
“Typically, more rainfall over a year will make plants happier and the ecosystem can support more vegetation,” said Feldman, the paper’s first author. “However, plants can shift their photosynthesis and growth by 10% to 30% if their rainfall input is changed, for example, from three drizzle events per week to one big rainstorm each week – even with the same total rainfall input over a year.”
Plants in intermediately wet regions like the Midwestern United States changed the most due to the altered rainfall, shifting function by 25% over a year.
Photosynthesis, greenness and growth had broadly varying responses to changing rainfall patterns from studies carried out across the globe. In 42% of cases, plants fared worse in the face of less frequent, more intense rainfall. In 35% of cases, plants improved, while in 23% of cases, plants stayed approximately the same.
This change in rain patterns is just one layer of climate change, Feldman said. Plants will also interact with other long-term climatic changes, including increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations and increasing air temperatures.
“Plants are responsible for the largest flux of carbon on global land,” he said. “These plant responses to daily rainfall variability will be critical to determine holistically because they influence crop yields and how much human-emitted carbon is taken up from the atmosphere.”
Feldman conducted the study along with colleagues from the University of Minnesota, Montana State University, Stanford University, Colorado State University, the U.S. Department of Agriculture and NASA Goddard Spaceflight Center.
Next, the team is working on a global analysis of how plants respond to changes to more intense, less frequent rainfall using different satellite measurements. They also plan to investigate whether plants have an optimal frequency of rainfall to which they may maximize their photosynthesis and growth.
“If we want to have any hope of accurately predicting the effects of more extreme rainfall on plants, we need to devote more work to understanding the underlying soil and plant processes that drive these different responses, especially at the timescale of individual rainstorms and the dry days in between,” said Feldman.
Journal Reference:
Feldman, A.F., Feng, X., Felton, A.J. et al. ‘Plant responses to changing rainfall frequency and intensity’, Nature Reviews Earth & Environment 5, 276–294 (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s43017-024-00534-0
Article Source:
Press Release/Material by University of Maryland
Featured image credit: frimufilms | Freepik.com




